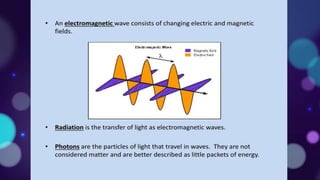
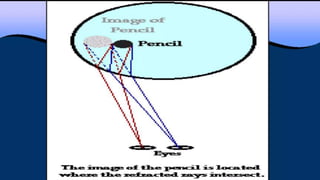
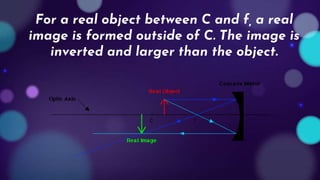
This document provides an overview of light and optics concepts. It begins with the nature of light and properties of light such as reflection and refraction. It then discusses Snell's law and its application to the refraction of light. The remainder of the document focuses on mirrors and lenses, including definitions of real and virtual images, examples of different types of curved mirrors and their imaging properties, as well as examples of convex and concave lenses and how they are used to correct vision. Worked examples are provided for solving problems using the mirror and lens equations.