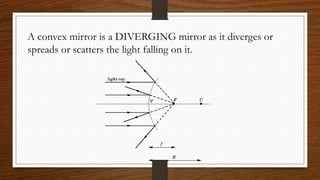
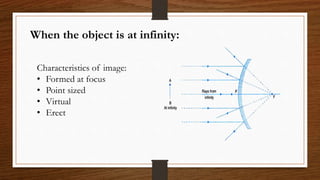
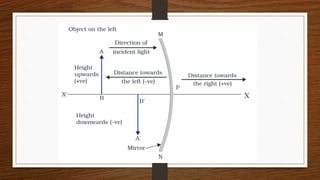
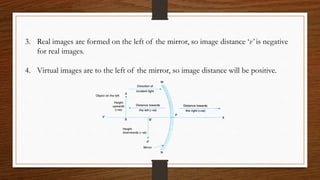
This document discusses ray diagrams and image formation using convex mirrors. It defines key terms like focal length and explains the characteristics of images formed by convex mirrors - always virtual, erect, diminished, and located between the pole and focus. Convex mirrors act as diverging mirrors and form images this way. The document also discusses uses of convex mirrors like in rear view mirrors in vehicles and the disadvantages of this application. In the end, it provides a recap of key concepts and formulas for mirrors.