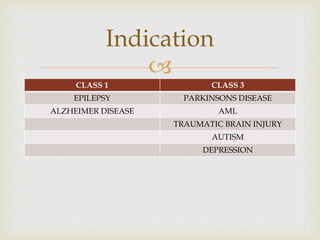
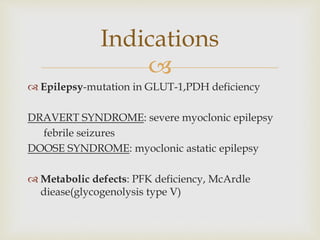
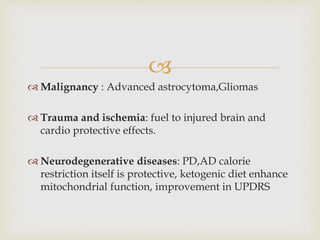
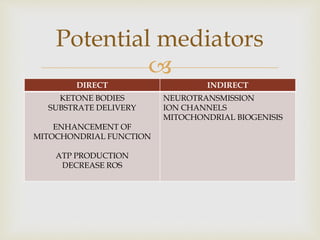
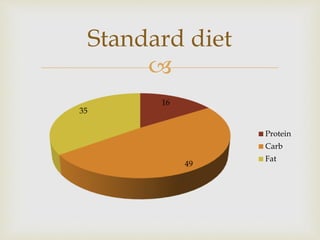
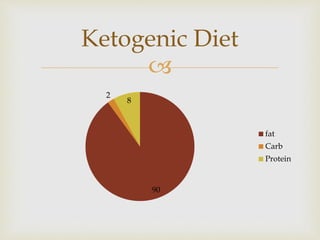
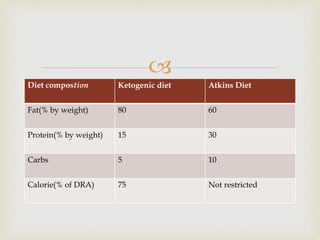
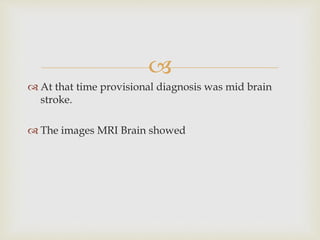
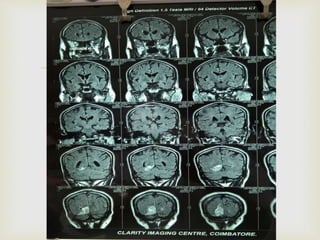
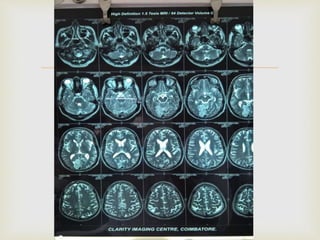
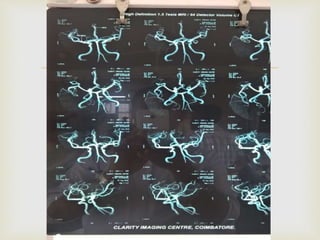
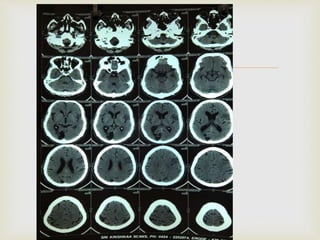
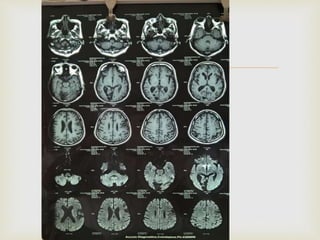
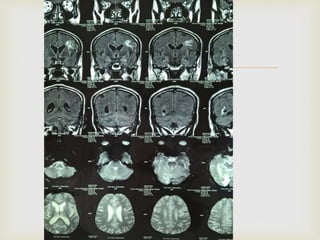
The ketogenic diet was initially developed in the 1920s to mimic the metabolic effects of fasting for treating epilepsy. It has since shown benefits for a variety of metabolic, oncologic, neurodegenerative, and psychiatric disorders through mechanisms like improving mitochondrial function and ATP production. Common indications for the ketogenic diet include epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, cancer, traumatic brain injury, autism, and depression. Side effects can include low-level acidosis, constipation, and nutrient deficiencies.