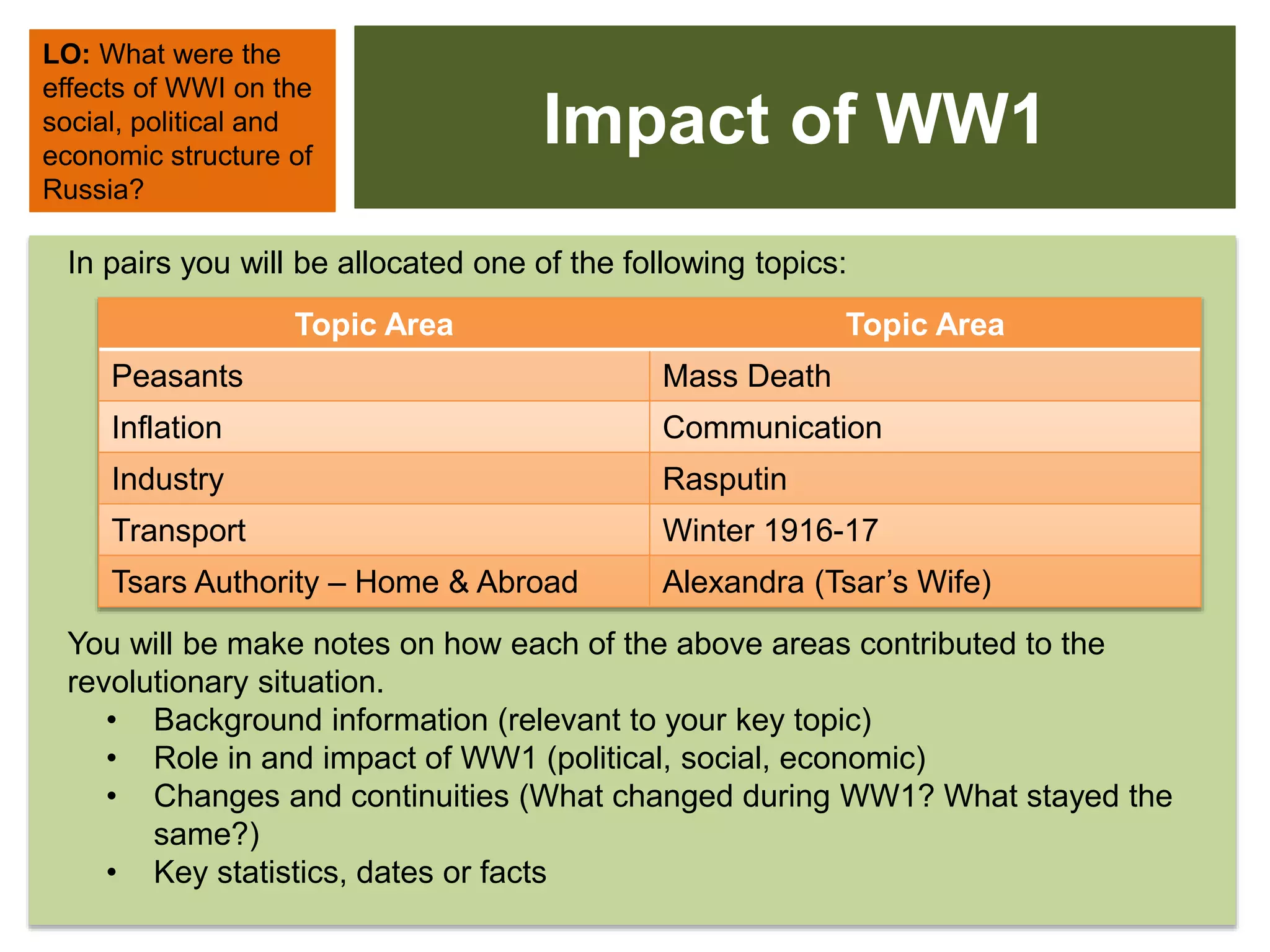
World War 1 had devastating impacts on Russia's social, political, and economic structure:
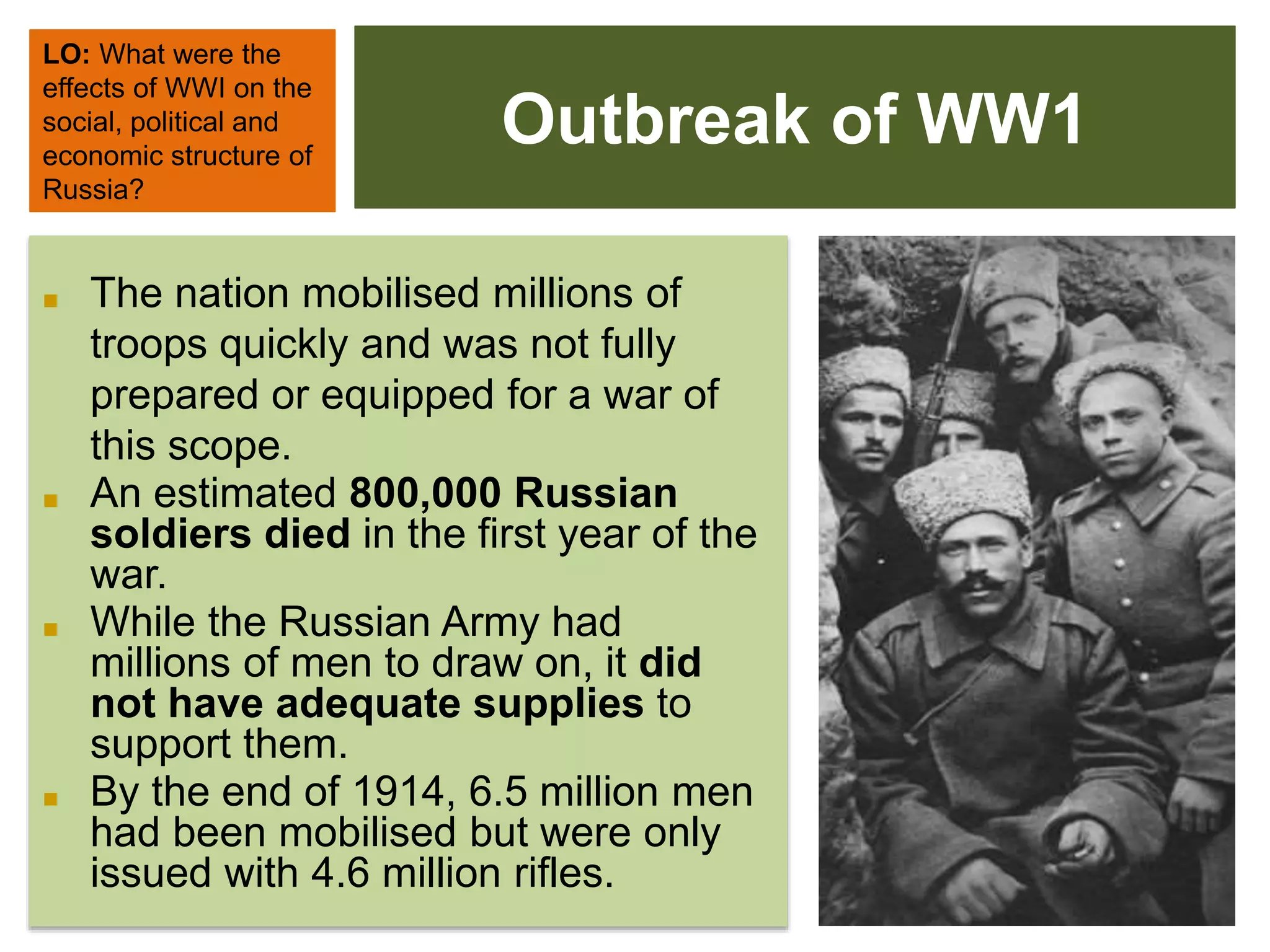
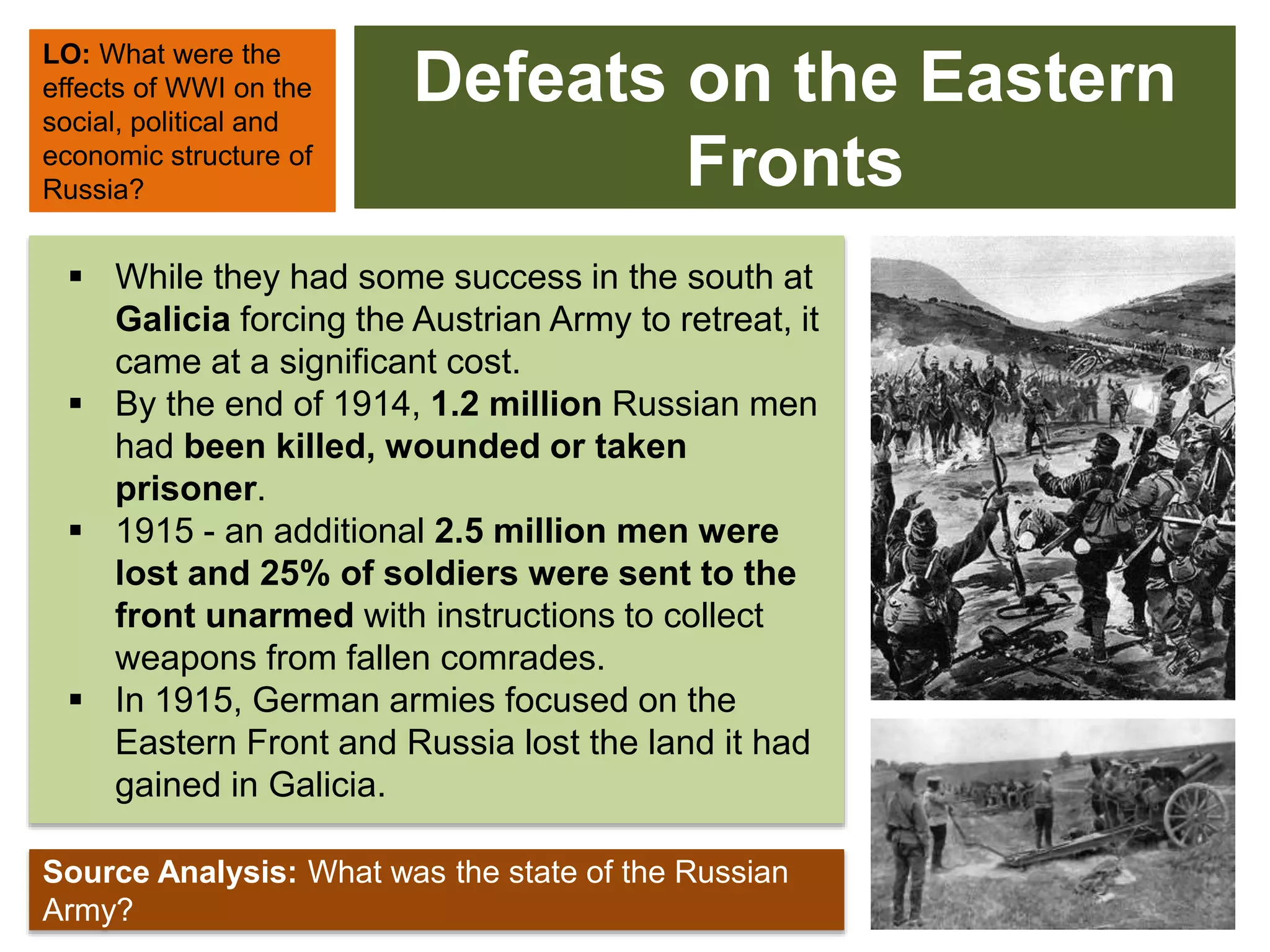
1) Military defeats weakened the Tsar's authority and led to massive casualties totaling over 1.7 million troops killed and 2.5 million captured by 1917.
2) The war effort strained Russia's economy through high spending, inflation, and transportation issues that caused food shortages in cities.
3) Social unrest grew as workers faced declining living standards from inflation, shortages, and loss of life. Over 25% of soldiers went to the front unarmed by 1915.