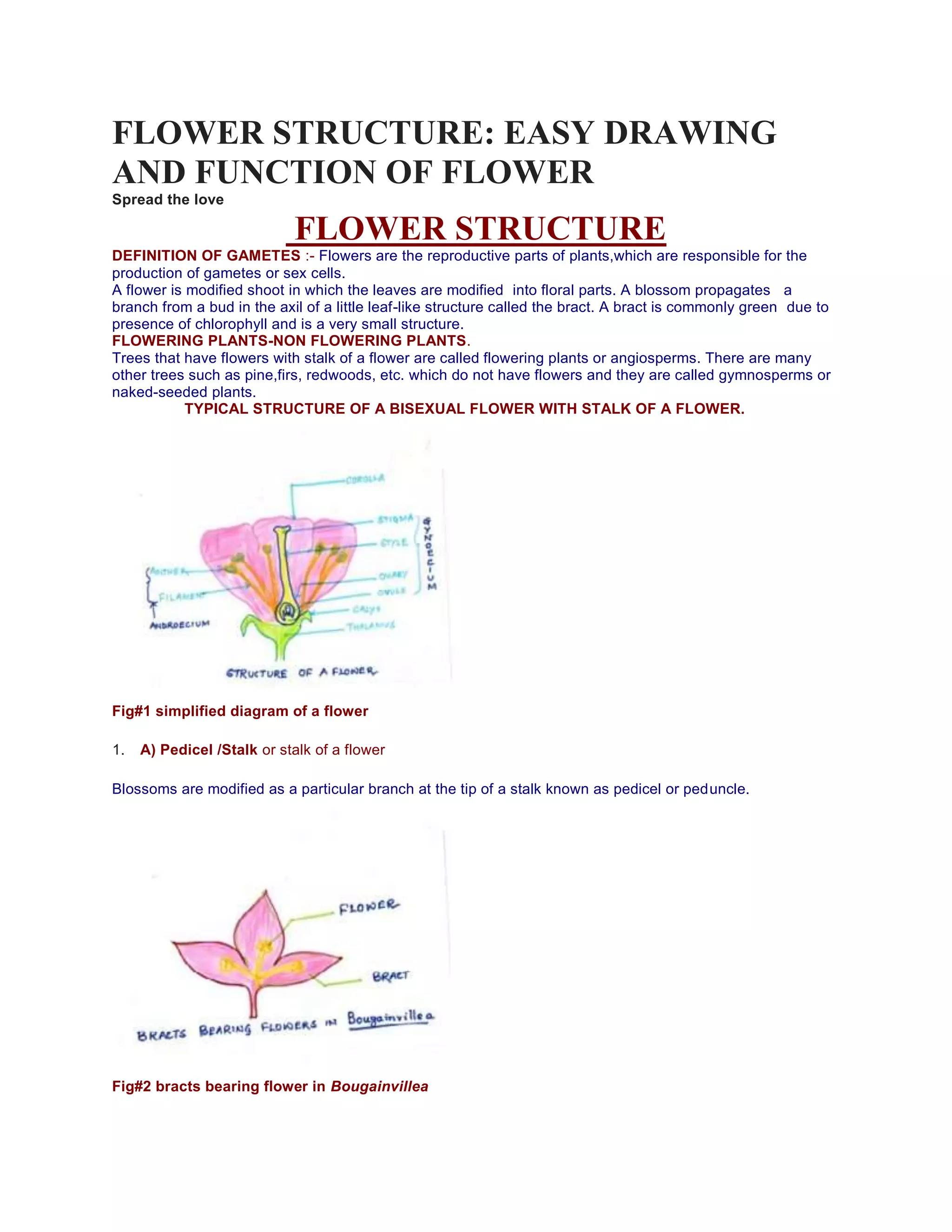
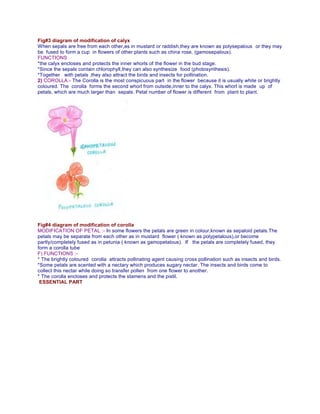
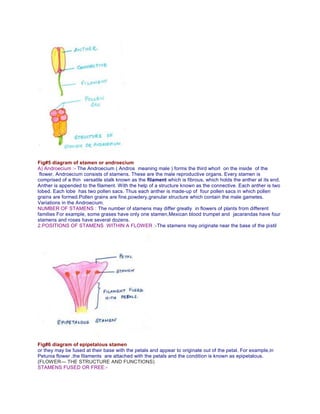
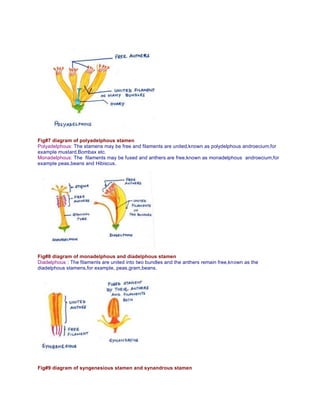
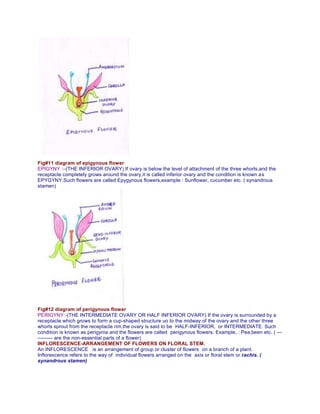
The document provides a detailed overview of flower structure, describing the essential and non-essential parts of flowers, including their functions and modifications. It categorizes flowers into angiosperms and gymnosperms, explaining the variations in structures like pedicel, receptacle, floral whorls, and reproductive organs. Additionally, it discusses the arrangement of flowers on floral stems, known as inflorescence, highlighting different classifications and characteristics within the plant reproductive system.