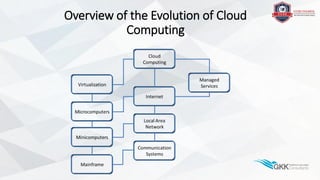
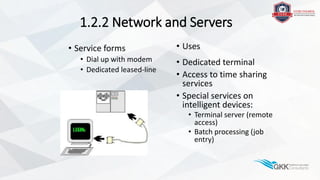
The document outlines the evolution of cloud computing from mainframe computers to modern networked systems. It discusses the development of minicomputers and microcomputers connected by local area networks. The role of the internet in enabling remote access to computing resources through protocols like TCP/IP is also covered. Virtualization technologies allowed efficient sharing of computing resources and led to the concept of cloud computing providing virtualized systems and storage over the internet.