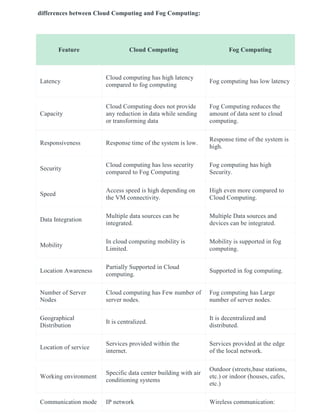
Cloud computing allows storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of on a local computer or server. It provides cost savings through a pay-as-you-go model without needing to own physical computing infrastructure. However, integrating cloud with IoT presents challenges like security issues due to resource-constrained IoT devices that cannot support complex encryption. Cloud-IoT integration also faces difficulties around data integration from diverse sources and ensuring communication across different devices and platforms. Effective strategies include using IoT SDKs, communication modules, local gateways, and cloud gateways to connect various types of devices to the cloud while addressing issues like latency, responsiveness, location awareness and mobility.