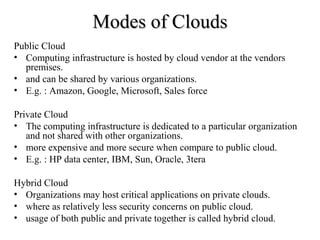
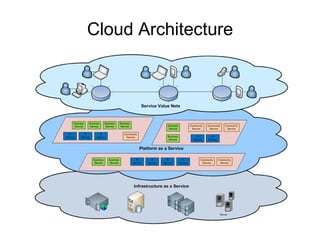
This document defines cloud computing as standardized IT capabilities delivered via the internet in a pay-per-use manner. It describes the main types of cloud models including public, private, and hybrid clouds. It also outlines the key cloud computing services, characteristics, architecture, operating systems, benefits, disadvantages, and major commercial cloud providers.