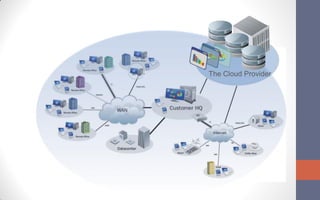
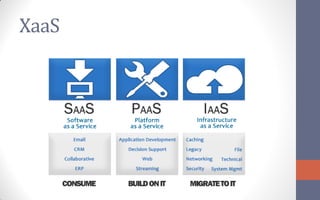
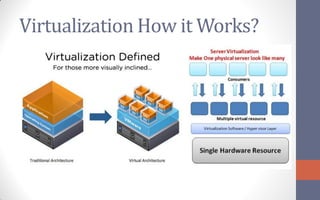
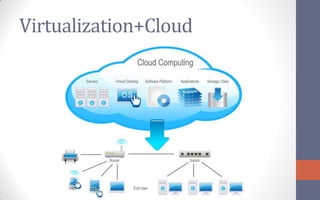
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as a network-based computing paradigm that leverages internet infrastructure to provide integrated services. It discusses the three primary approaches to cloud computing: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), with a focus on the critical role of virtualization in enhancing scalability and efficiency. The conclusion emphasizes the future importance of cloud computing regarding cost, performance, data security, and service agreements.