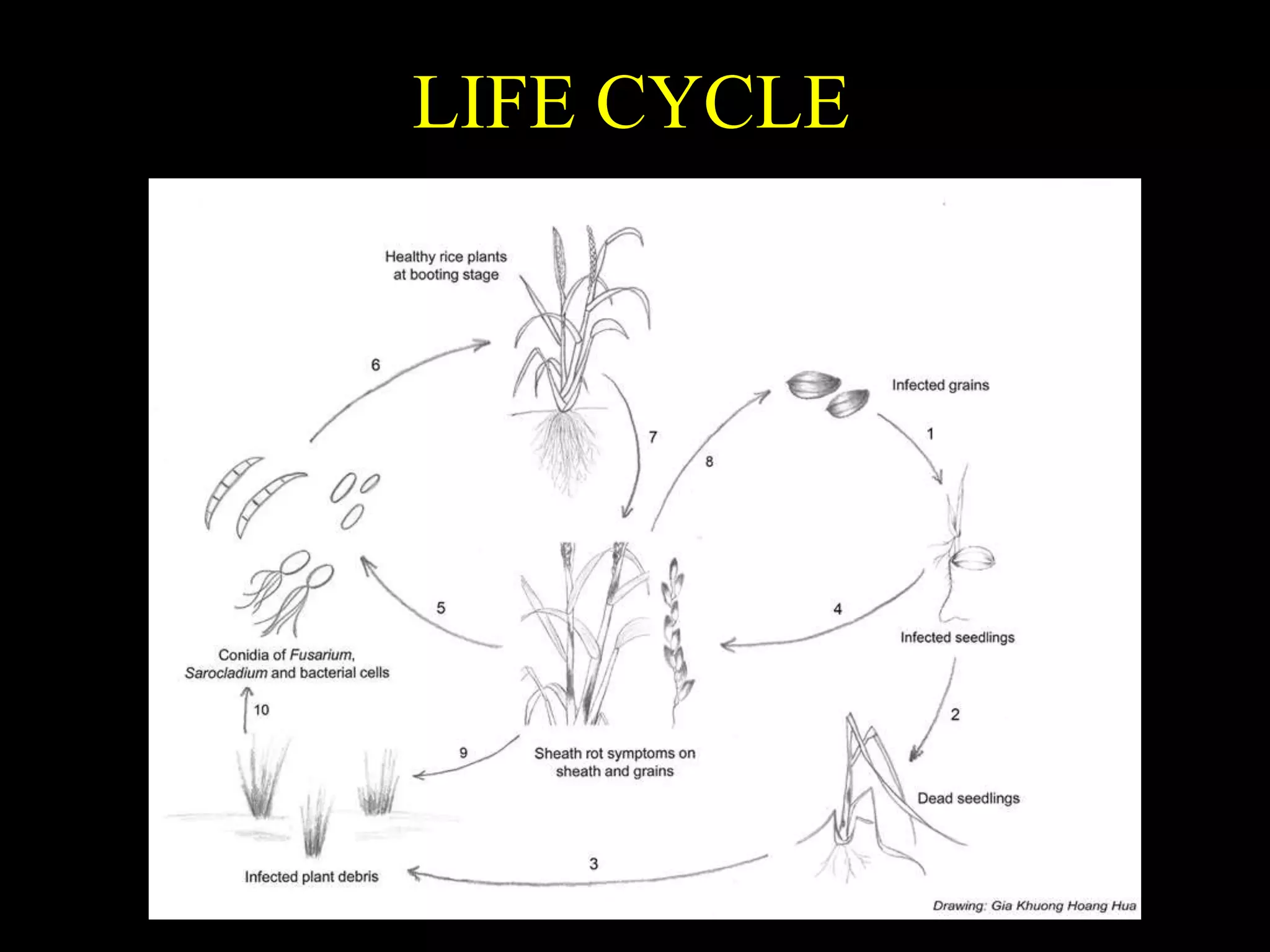
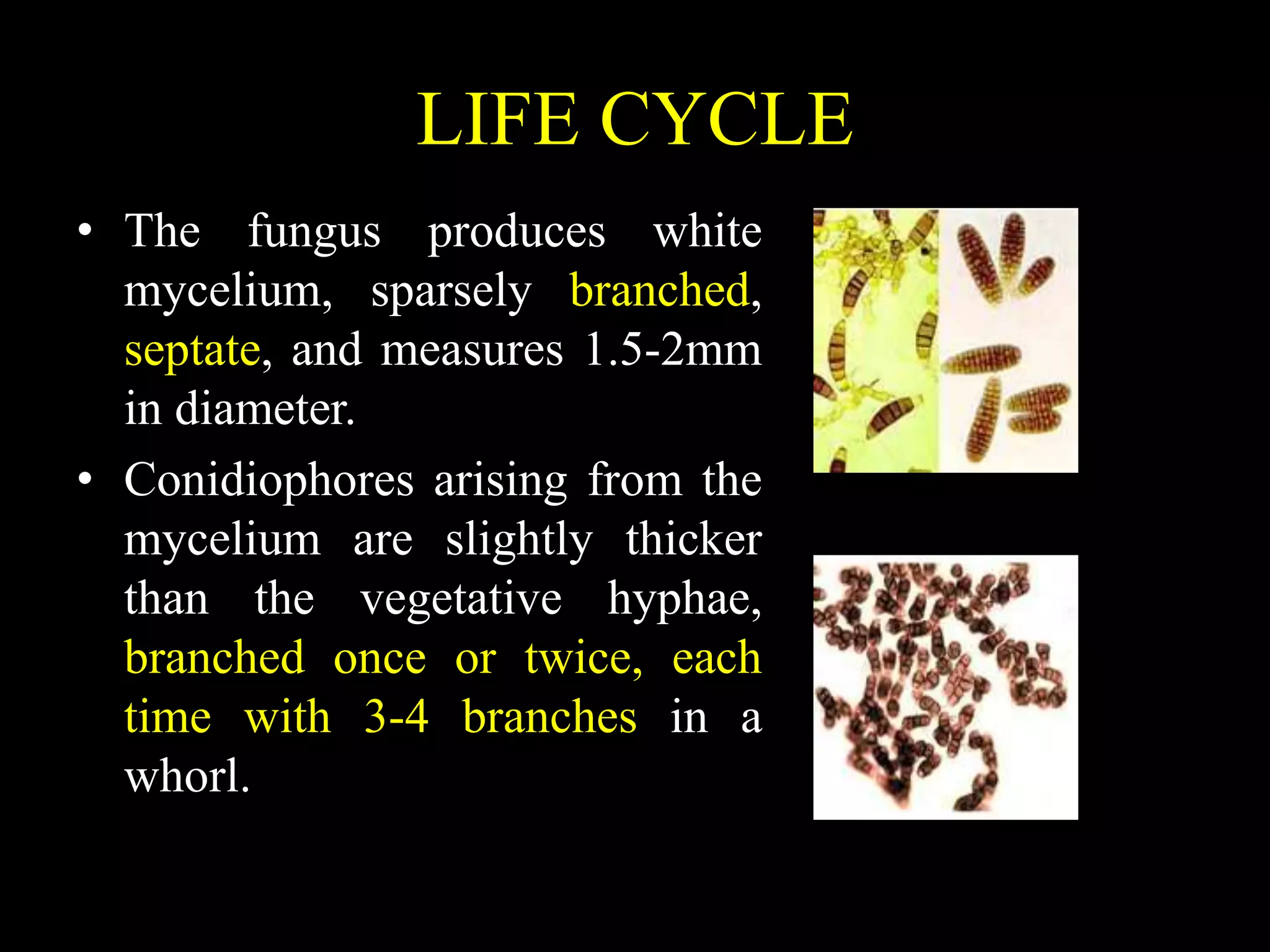
1. Sarocladium oryzae is a fungus that causes sheath rot disease in rice. It has 10 known species and is the type species for the genus Sarocladium.
2. The fungus produces toxins that induce chlorosis and reduce seed viability. It infects rice through wounds or stomata and grows intercellularly.
3. Symptoms of sheath rot disease include discolored leaf sheaths with lesions, unemerged panicles remaining in sheaths, and sterile or discolored grains. The disease impacts rice during heading and maturity.