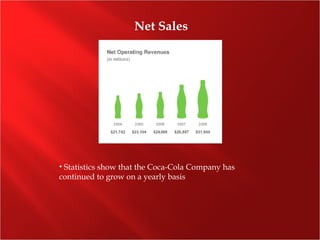
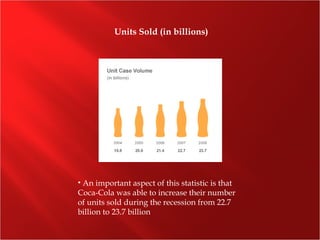
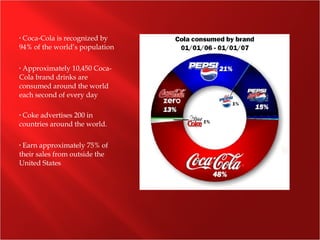
The Coca-Cola Company was founded in 1886 and is the world's largest beverage company. It manufactures concentrates and syrups that are then sold to bottlers who package and distribute over 400 brands of drinks in over 200 countries. While carbonated soft drinks make up most sales, the company has expanded its portfolio to include water, juice, tea, and sports drinks. Coca-Cola has maintained its dominance through effective marketing campaigns, strategic partnerships and acquisitions, and a focus on international growth.