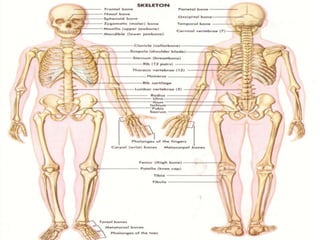
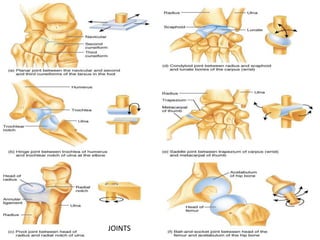
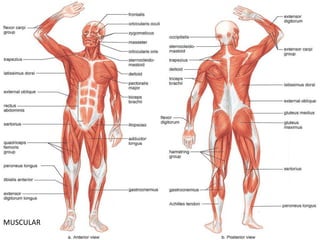
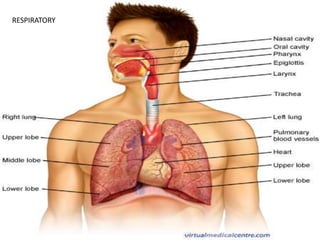
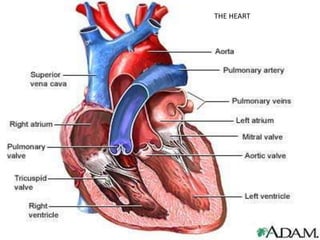
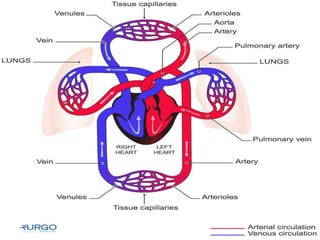
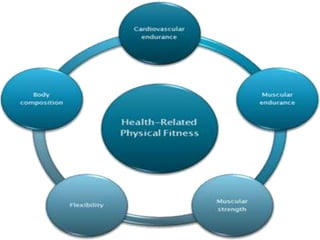
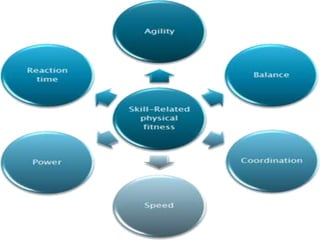
This document discusses the body's systems involved in motion. It describes the joints, muscles, respiratory and cardiovascular systems. It then outlines some immediate physiological responses to exercise training like changes in heart rate, ventilation rate, stroke volume and cardiac output. Finally, it discusses different types of motion like linear and velocity, as well as concepts like momentum, balance, stability, and fluid mechanics.