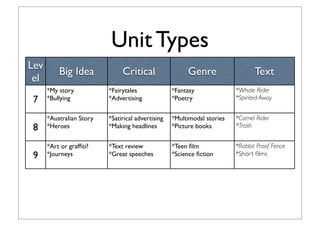
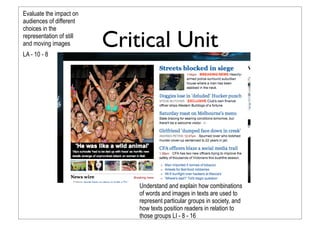
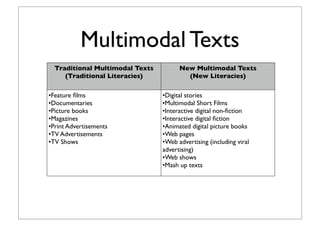
The document discusses recommendations for effective units to teach English for years 7-9 based on the Australian curriculum. It suggests focusing units on big ideas, critical awareness, genres/text types, and responding to texts. Example unit topics are listed for each area and year level. Multimodal texts and those exploring cross-curriculum priorities like sustainability are also recommended resources. The goal is to do fewer things in the curriculum but explore those topics in more depth so students better master key concepts and skills.