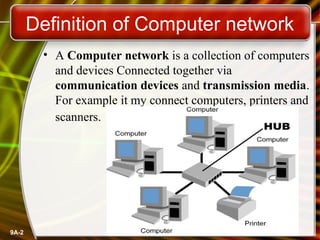
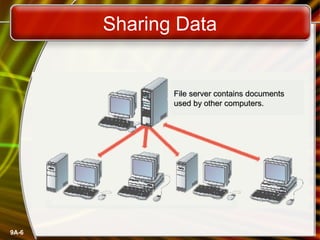
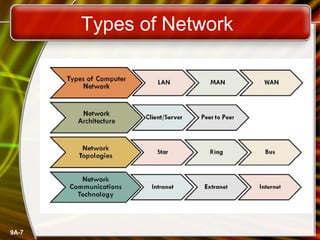
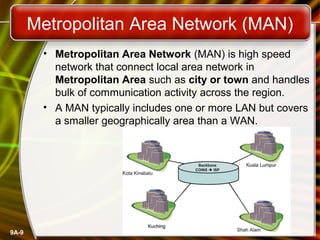
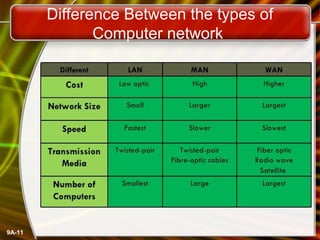
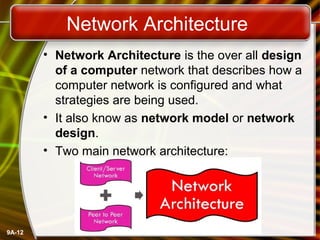
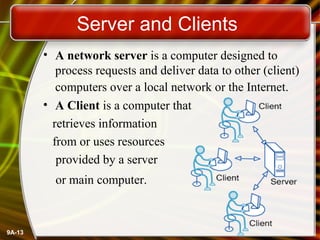
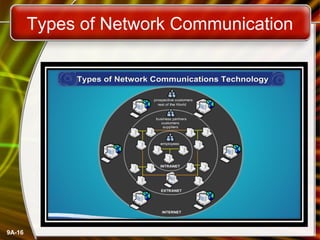
A computer network connects computers and devices together through communication devices and transmission media. Communication describes the transfer of data, instructions, and information between two or more computers or devices. There are several types of computer networks including local area networks (LANs) that connect devices in a limited geographic area like a home or office, metropolitan area networks (MANs) that connect LANs across a region like a city, and wide area networks (WANs) that span large geographic areas like countries. Networks can be used to share resources like printers and files, provide communication services, and allow access to information from any connected device. However, larger networks are more difficult to manage and viruses could potentially spread between connected systems.