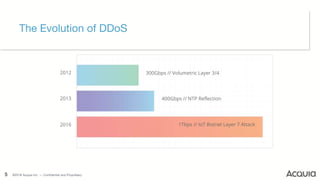
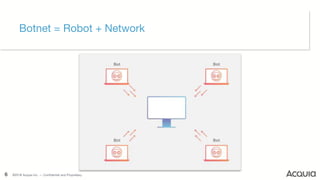
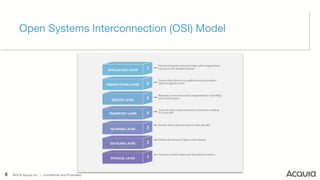
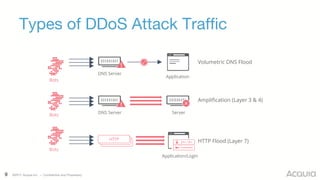
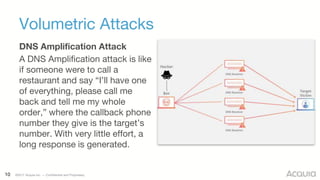
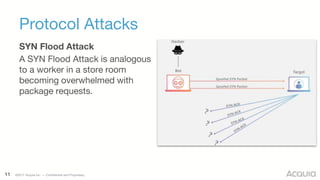
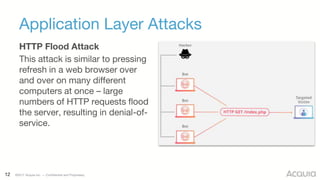
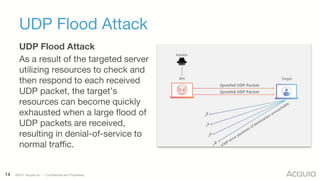
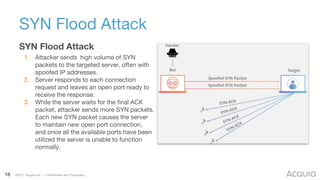
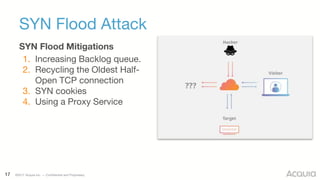
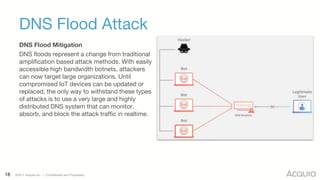
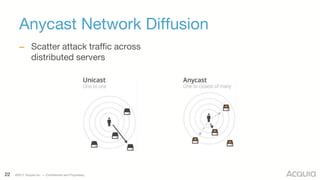
The document discusses the nature, evolution, and mitigation of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, highlighting examples of historic attacks, including a significant 400 Gbps attack in 2016. It explains how attackers utilize botnets to overwhelm targets, outlines various types of DDoS attacks, and describes potential mitigation strategies such as rate limiting and anycast networks. The document serves as a comprehensive overview of DDoS threats and protection measures relevant to organizations.

![3 ©2017 Acquia Inc. — Confidential and Proprietary
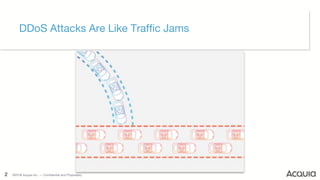
Elements of a DDoS Attack
– Malicious attempt to
disrupt normal traffic
– Overwhelm target with
flood
– Utilize multiple
compromised systems
– Motive can be political,
social, or financial
– Targets in every industry
Subject: ddos attack
Hi!
If you dont pay 8 bitcoin until 17.
january your network will be hardly
ddosed! Our attacks are super powerfull.
And if you dont pay until 17.
january ddos attack will start and price
to stop will double!
We are not kidding and we will do small
demo now on [XXXXXXXX] to show we are
serious.
Pay and you are safe from us forever.
OUR BITCOIN ADDRESS: [XXXXXXXX]
Dont reply, we will ignore! Pay and we
will be notify you payed and you are
safe.
Cheers!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinaranatomyofaddosattack-171208133706/85/The-Anatomy-of-DDoS-Attacks-3-320.jpg)