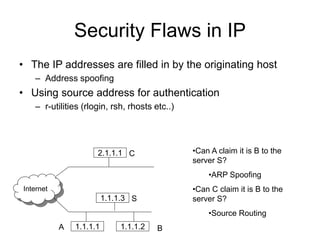
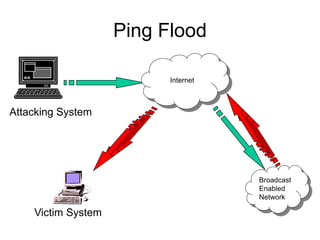
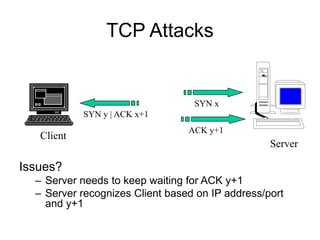
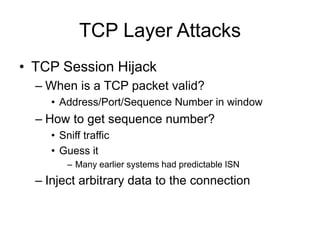
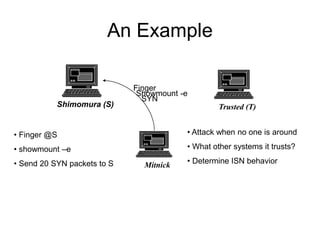
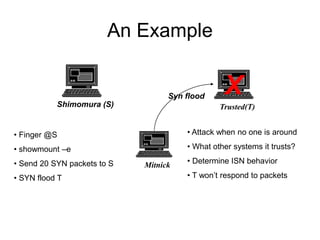
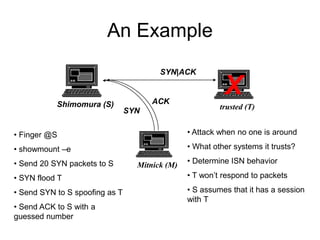
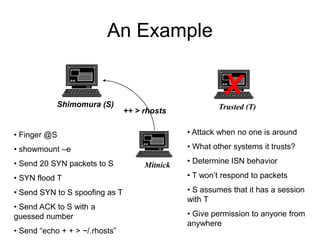
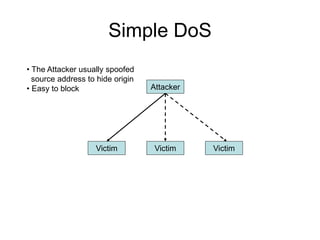
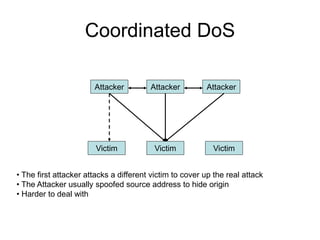
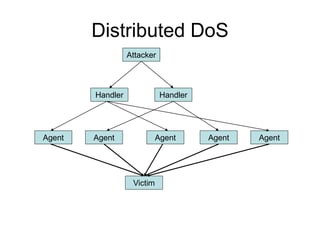
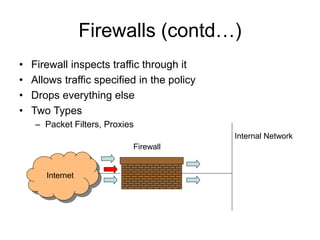
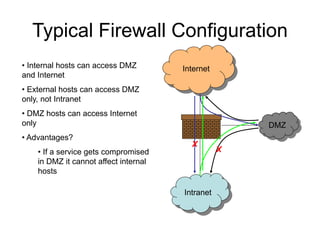
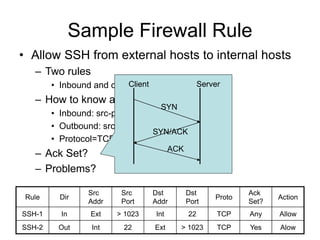
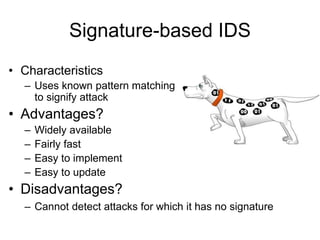
This document provides an overview of network security concepts including vulnerabilities, denial of service attacks, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. It discusses how TCP/IP was not initially designed with security in mind and is vulnerable to spoofing and man-in-the-middle attacks. Denial of service attacks like SYN flooding aim to overwhelm servers through excessive connection requests. Firewalls use packet filtering and proxies to restrict network access and traffic based on security rules. Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic to identify attacks and anomalies beyond what is allowed by firewall rules.