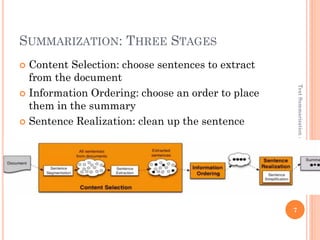
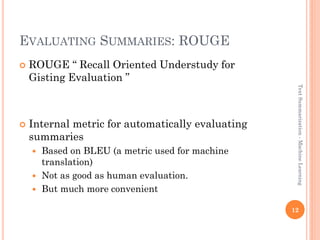
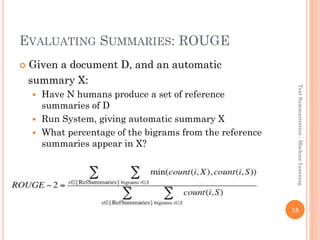
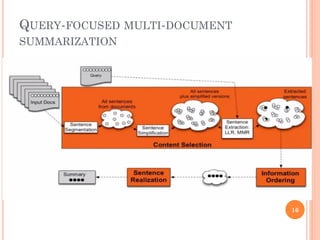
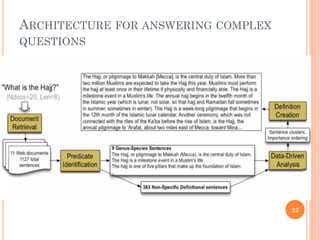
This document discusses text summarization using machine learning. It begins by defining text summarization as reducing a text to create a summary that retains the most important points. There are two main types: single document summarization and multiple document summarization. Extractive summarization creates summaries by extracting phrases or sentences from the source text, while abstractive summarization expresses ideas using different words. Supervised machine learning approaches use labeled training data to train classifiers to select content, while unsupervised approaches select content based on metrics like term frequency-inverse document frequency. ROUGE is commonly used to automatically evaluate summaries by comparing them to human references. Query-focused multi-document summarization aims to answer a user's information need by summarizing relevant documents