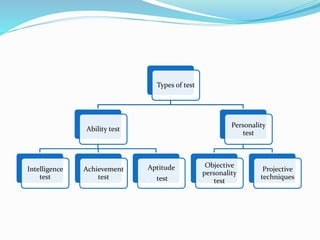
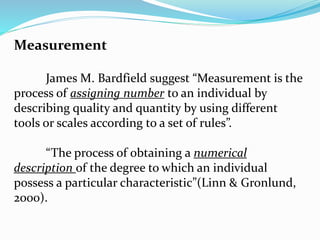
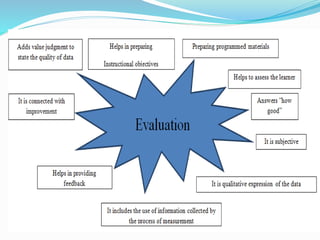
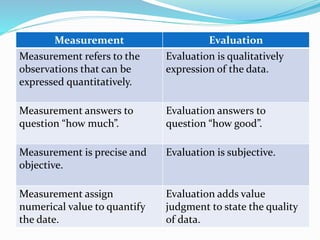
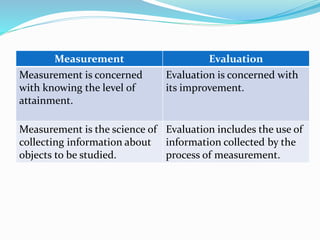
The document discusses the importance of testing, measurement, and evaluation in education, emphasizing their roles in assessing student abilities and progress. Testing is defined as a systematic procedure to evaluate individual performance, while measurement quantitatively describes traits, and evaluation qualitatively assesses whether educational objectives have been met. It contrasts measurement and evaluation, noting that measurement provides numerical data, whereas evaluation involves subjective judgments about quality and improvement.