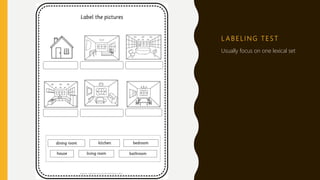
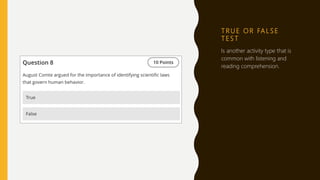
This document discusses testing, assessment, and evaluation in educational systems. It defines key terms like testing, assessment, and evaluation. It also describes different types of common tests for primary students like placement, diagnostic, and progress tests. The document outlines characteristics of good tests, such as construct validity, face validity, reliability, and practicality. Finally, it provides examples of different types of tests, including labeling, cloze, matching, multiple choice, true or false, numbering items in sequence, question and answer, and sentence writing/completion tests.