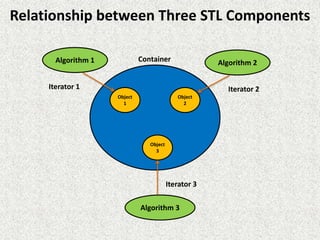
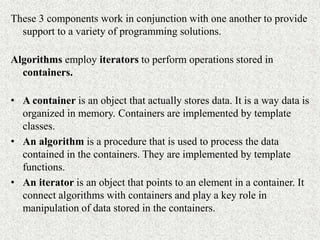
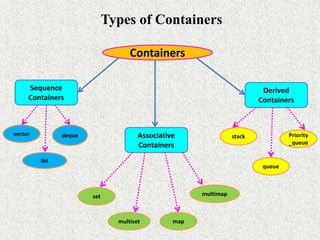
The document discusses the Standard Template Library (STL) in C++. It describes the three key components of STL - containers, algorithms, and iterators. Containers like vectors, lists, and maps are used to store and organize data. Algorithms perform operations on data stored in containers. Iterators are used by algorithms to access container elements. The containers, algorithms, and iterators work together to provide support for various programming solutions.