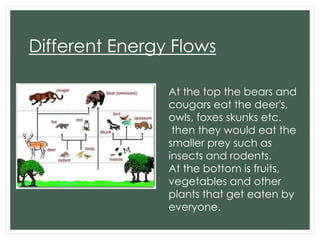
Temperate deciduous forests are characterized by trees that lose their leaves seasonally. Common trees include birch and oak, while animals include chipmunks, deer, and coyotes. These forests experience distinct seasons and are found worldwide. Pollution can accumulate in these ecosystems. Invasive species like the citrus long-horned beetle from Asia damage trees. Energy flows from plants and smaller prey eaten by larger predators like bears and cougars. Biotic relationships include mutualism between blackberry bushes and bees, commensalism between chipmunks and trees, and parasitism like bears eating fish. Succession occurs naturally after disturbances through regrowth from seeds and stumps. Predator-prey interactions include