1. Telescopes use different types of lenses and mirrors to collect light from space and study the universe.
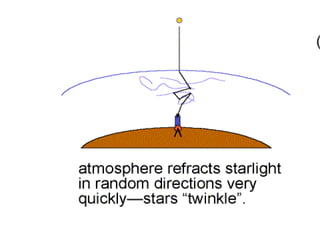
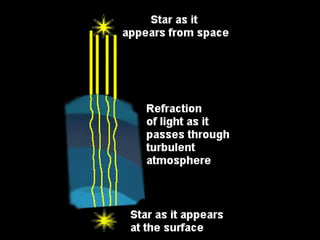
2. The location and environment of telescopes is important, with large telescopes placed in high altitude observatories for protection and to reduce atmospheric interference.
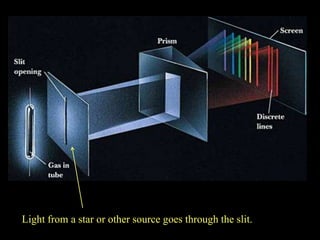
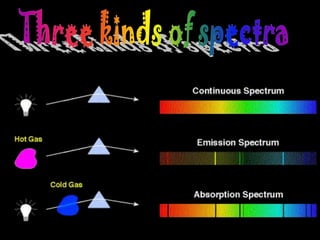
3. Telescopes study different wavelengths of light beyond what is visible to gather additional information, with certain types best suited for specific targets like new stars or black holes.