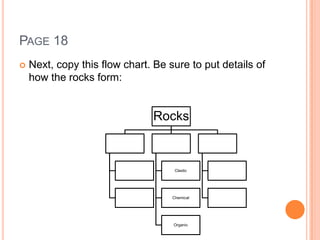
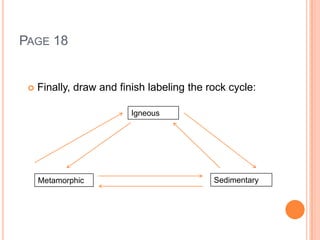
This document provides information about classifying and identifying rocks and minerals. It includes directions for an in-class activity where students will classify rocks, label the rock cycle, and answer questions about rock and mineral formation. It also describes a review game where students answer questions as a group about topics like the three main rock types, what rocks are made of, how rocks are used, and processes involved in the rock cycle.