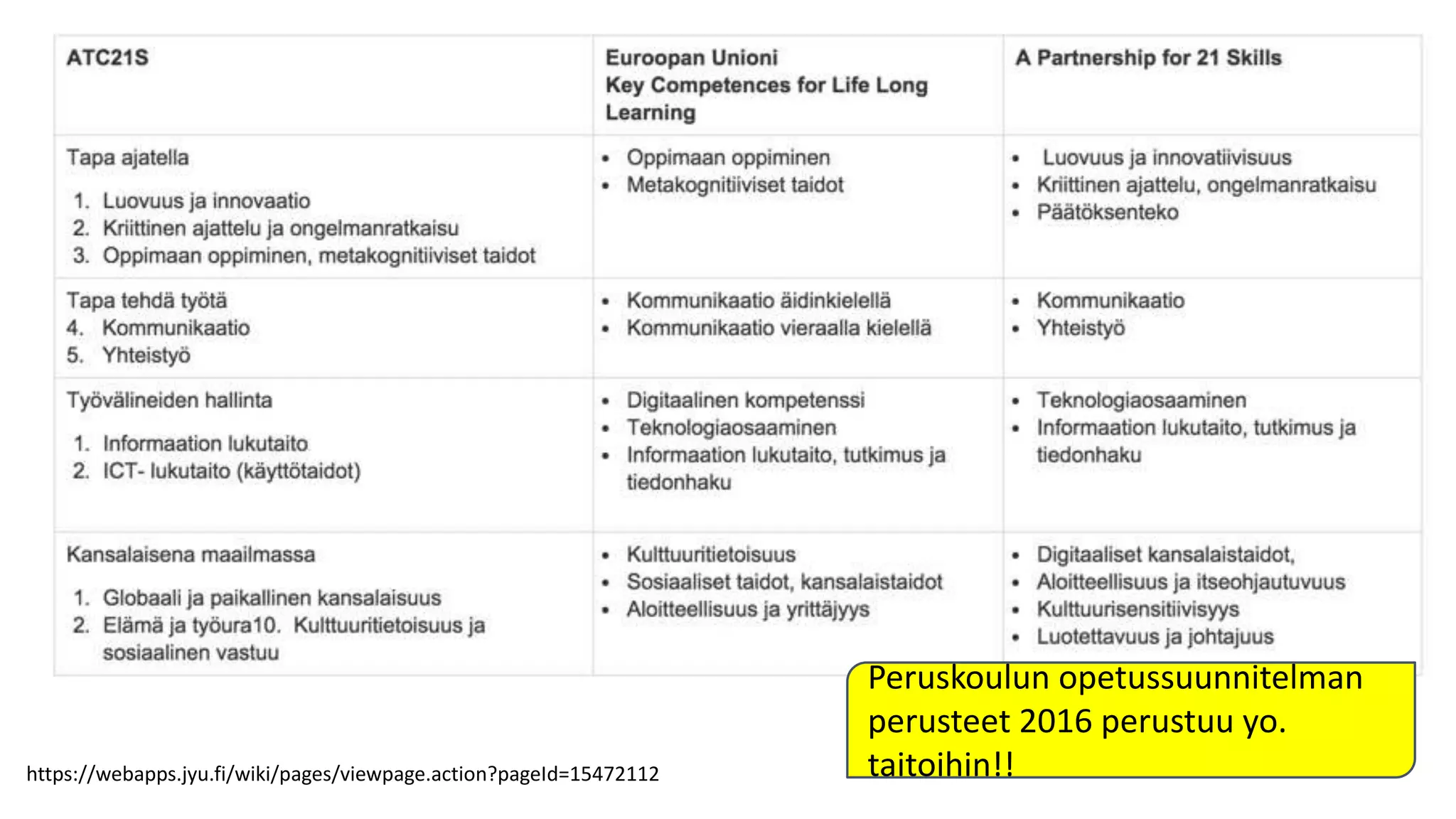
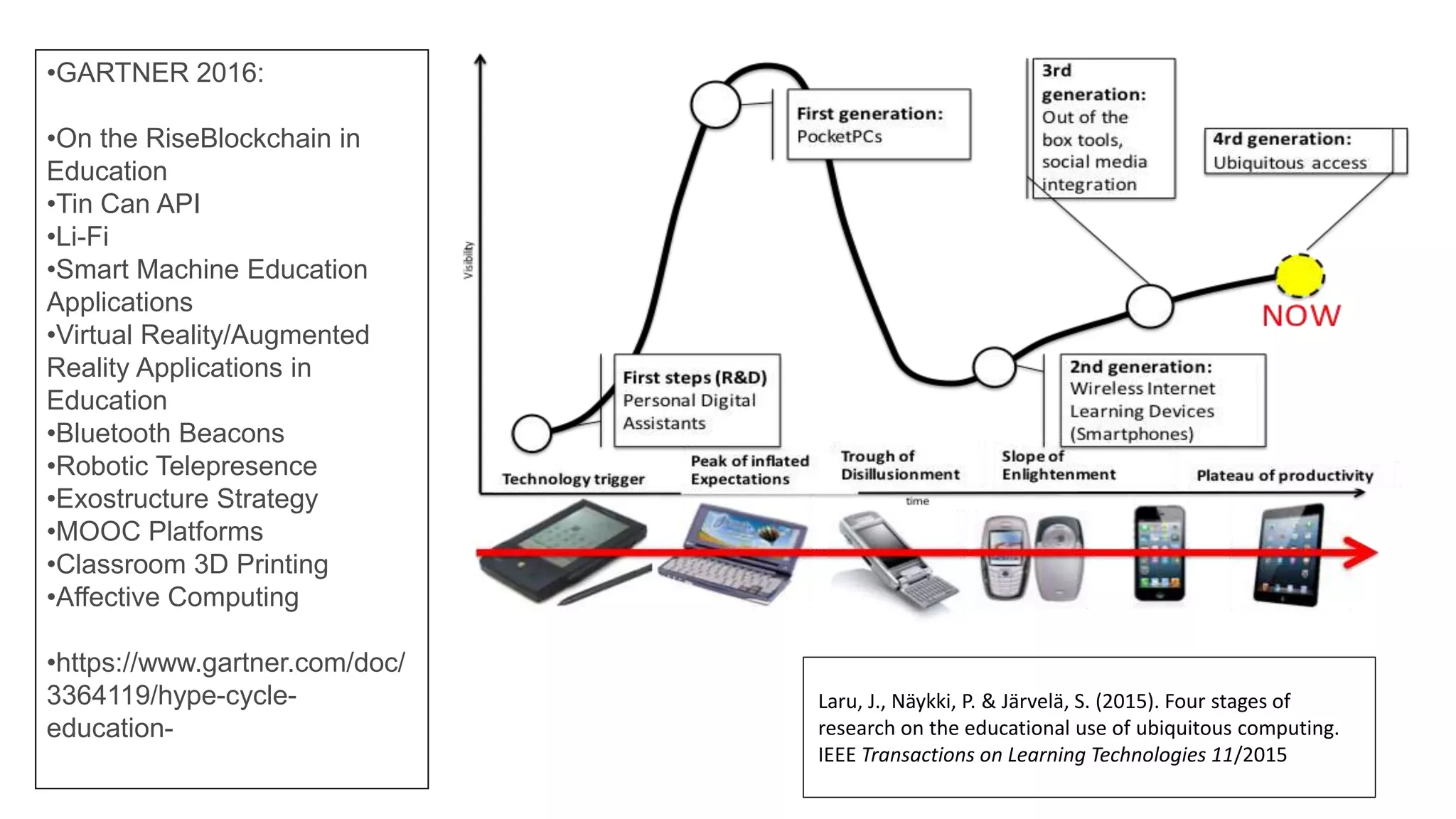
The document discusses the integration of technology in education, highlighting the importance of technology-supported learning and various educational tools. It references numerous studies and resources related to Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), student retention, and the evolving landscape of educational methodologies. Additionally, it touches on educational strategies and the necessity for adaptive learning environments to enhance teaching effectiveness.