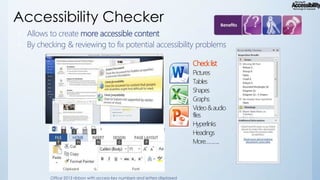
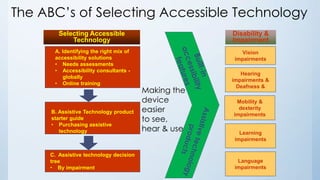
The document outlines Microsoft's commitment to accessibility, emphasizing the need for technology and educational tools that cater to individuals with disabilities. It discusses various disability statistics, accessibility features, and the importance of creating inclusive learning environments through personalized approaches. Additionally, it highlights relevant policies and Microsoft's strategies in developing accessible technologies and ensuring that all students have equal educational opportunities.