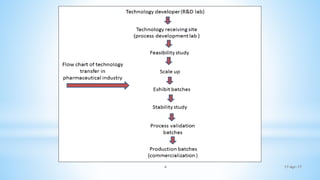
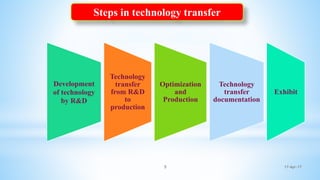
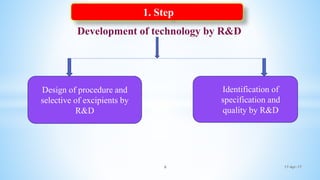
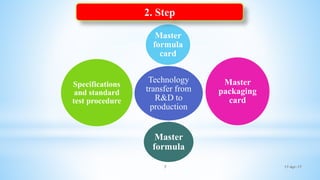
The document evaluates technology transfer approaches for solid dosage forms from R&D to manufacturing, outlining steps for effective transfer, the importance of knowledge sharing, and the impact on production quality. It highlights the aim to enhance manufacturing capacity and identifies potential gaps in knowledge required for successful implementation. The expected outcomes include adherence to WHO guidelines and various references discussing technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry.