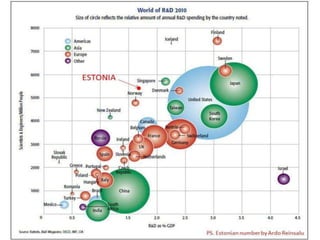
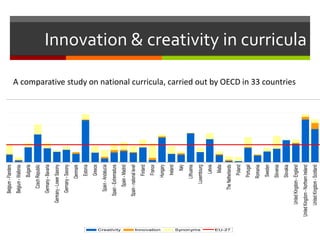
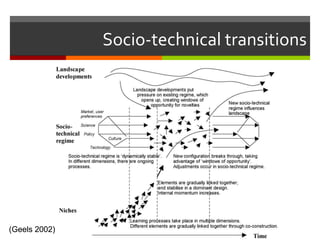
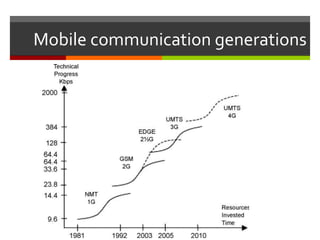
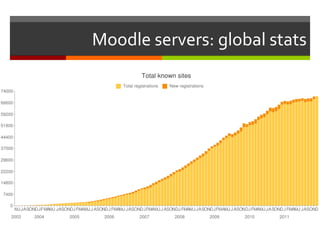
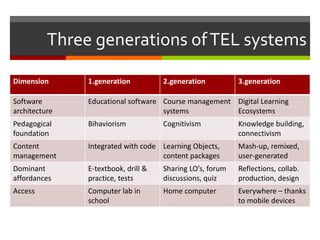
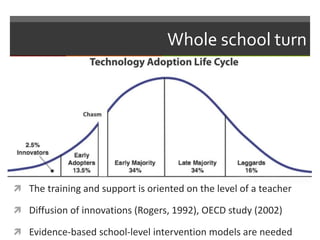
This document discusses technology and innovation in curriculum. It defines innovation and describes different types including product, process, organizational, and market innovation. It provides examples of innovation in Estonia including boosting the IT industry through incubators, start-ups, and hackathons. The document also discusses innovation in schools, with examples focusing on participatory and anticipatory learning. It outlines Estonia's national curriculum requirements for technology and innovation as a cross-curricular theme and provides sample project scenarios. Finally, it discusses tools and strategies to support innovative teaching and a digital turn in education.