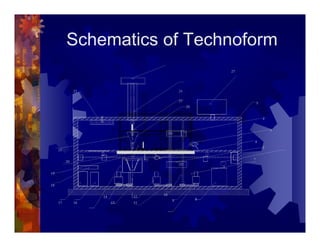
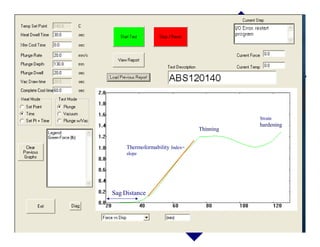
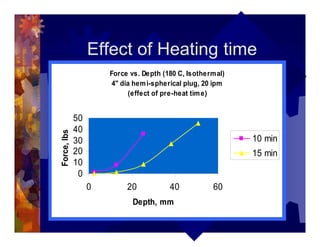
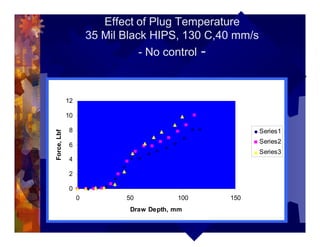
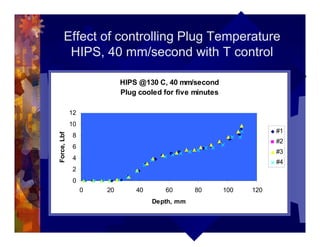
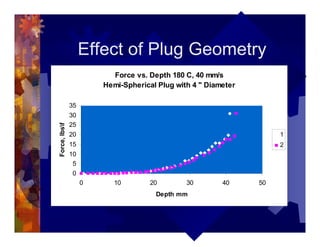
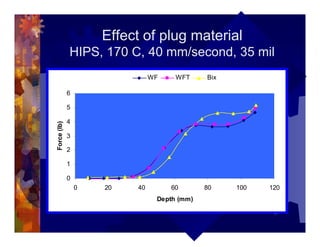
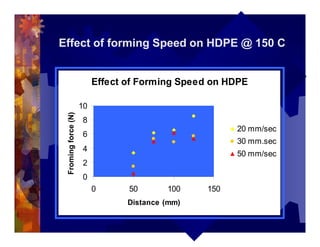
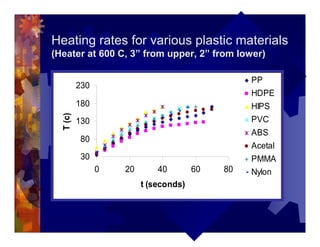
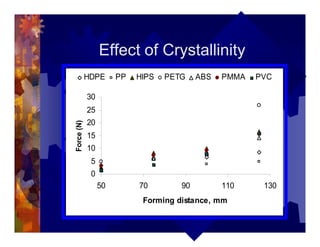
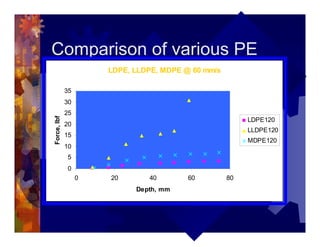
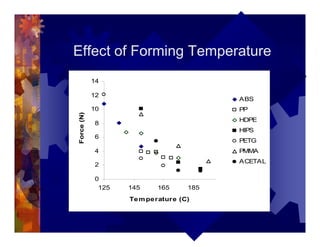
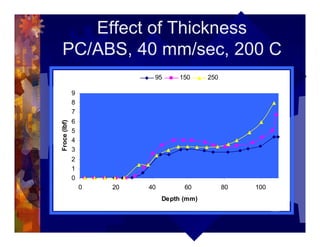
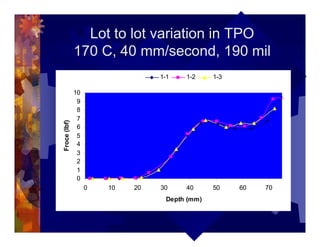
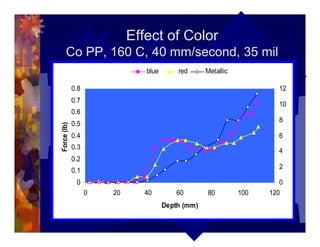
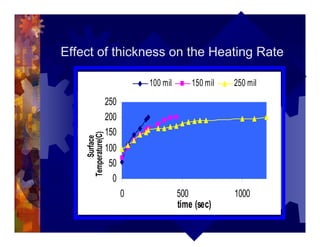
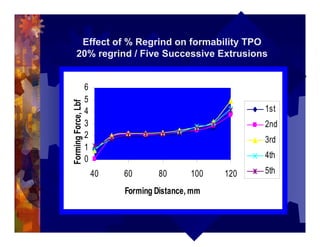
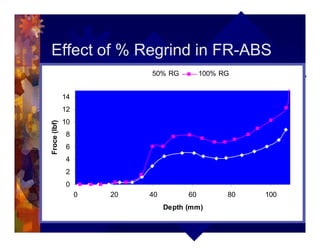
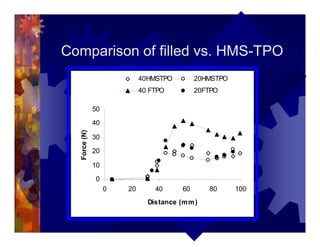
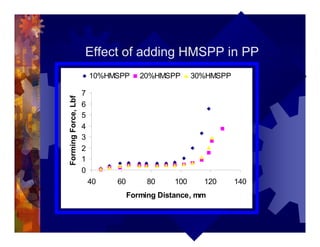
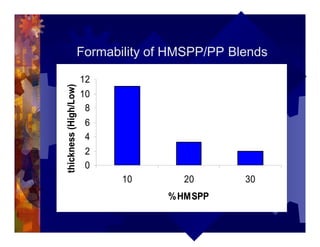
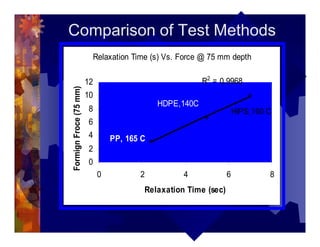
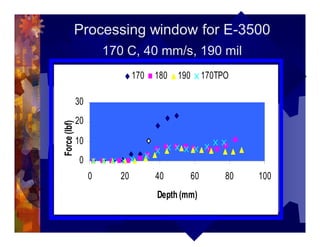
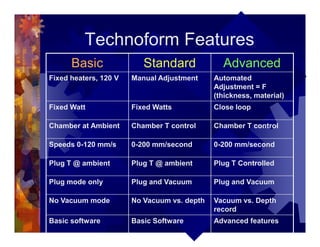
The document describes a new thermoformability testing device called Technoform. It aims to address limitations of current testing methods by evaluating materials under conditions that closely mimic the full thermoforming process. Technoform tests specimens through heating, 3D stretching, forming, and cooling. It provides quantitative data on various metrics like sag distance, forming force, and shrinkage. The document outlines Technoform's design and capabilities, and provides several examples showing how it can evaluate the effects of various material and process parameters on thermoformability.