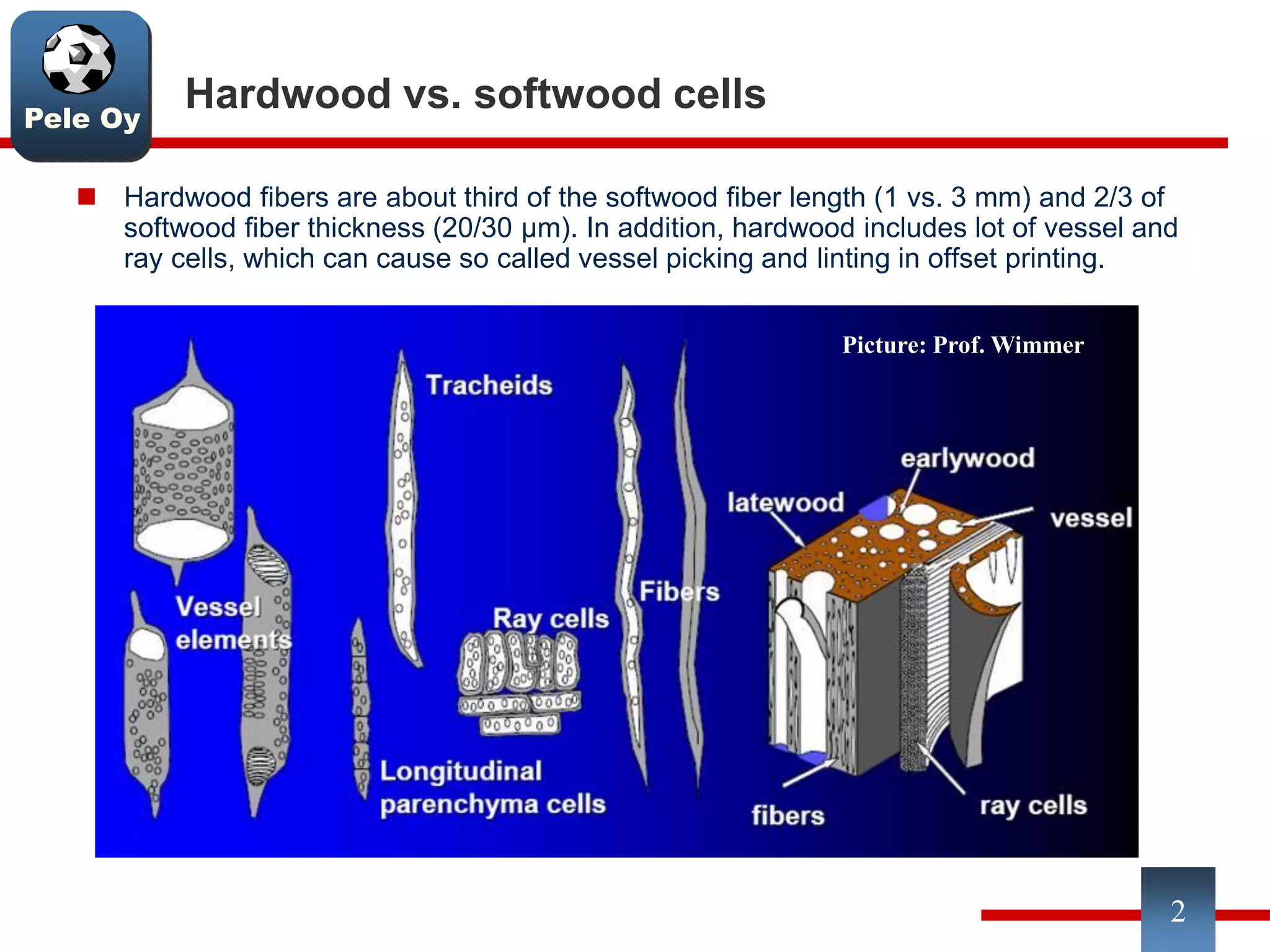
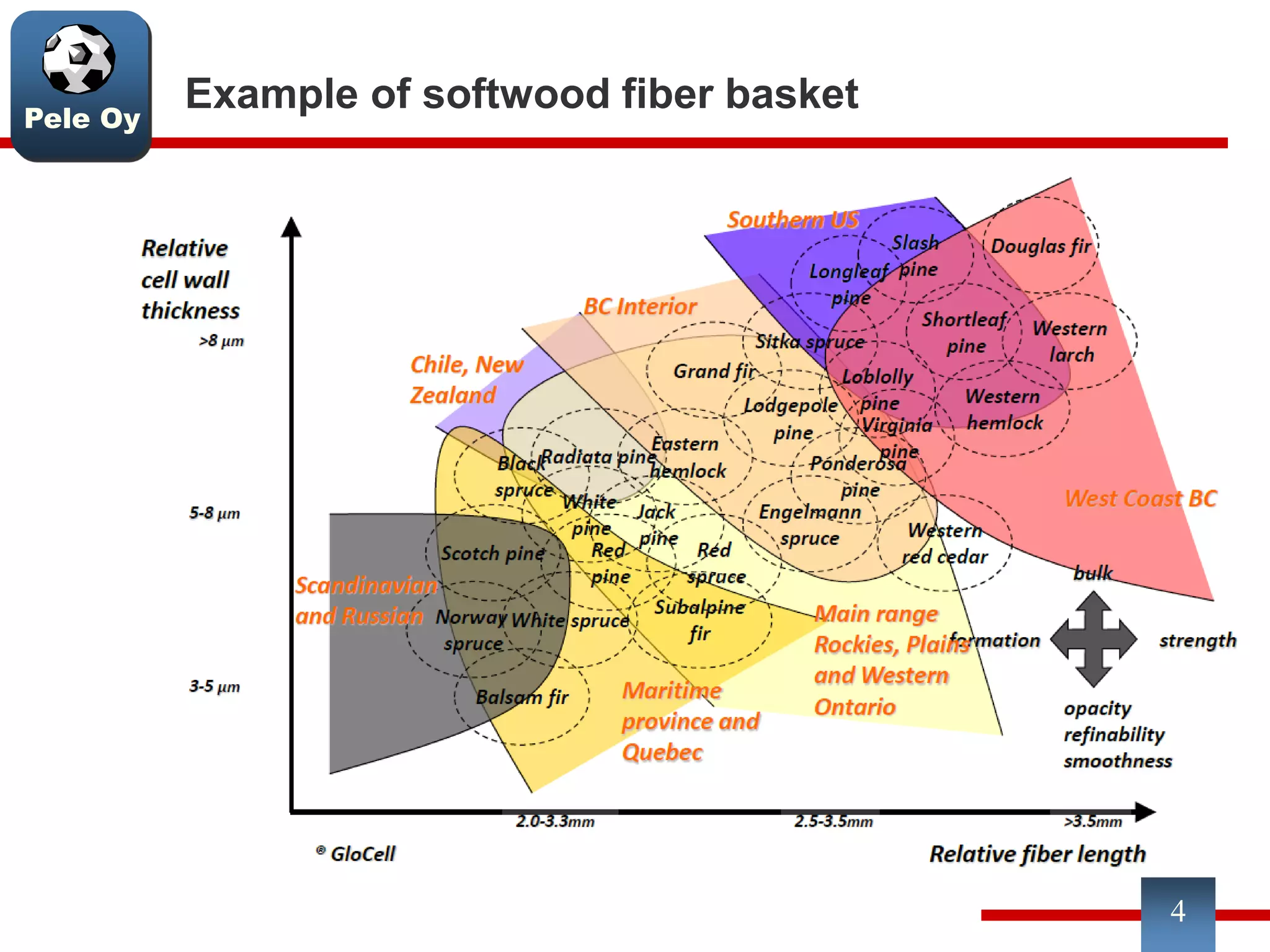
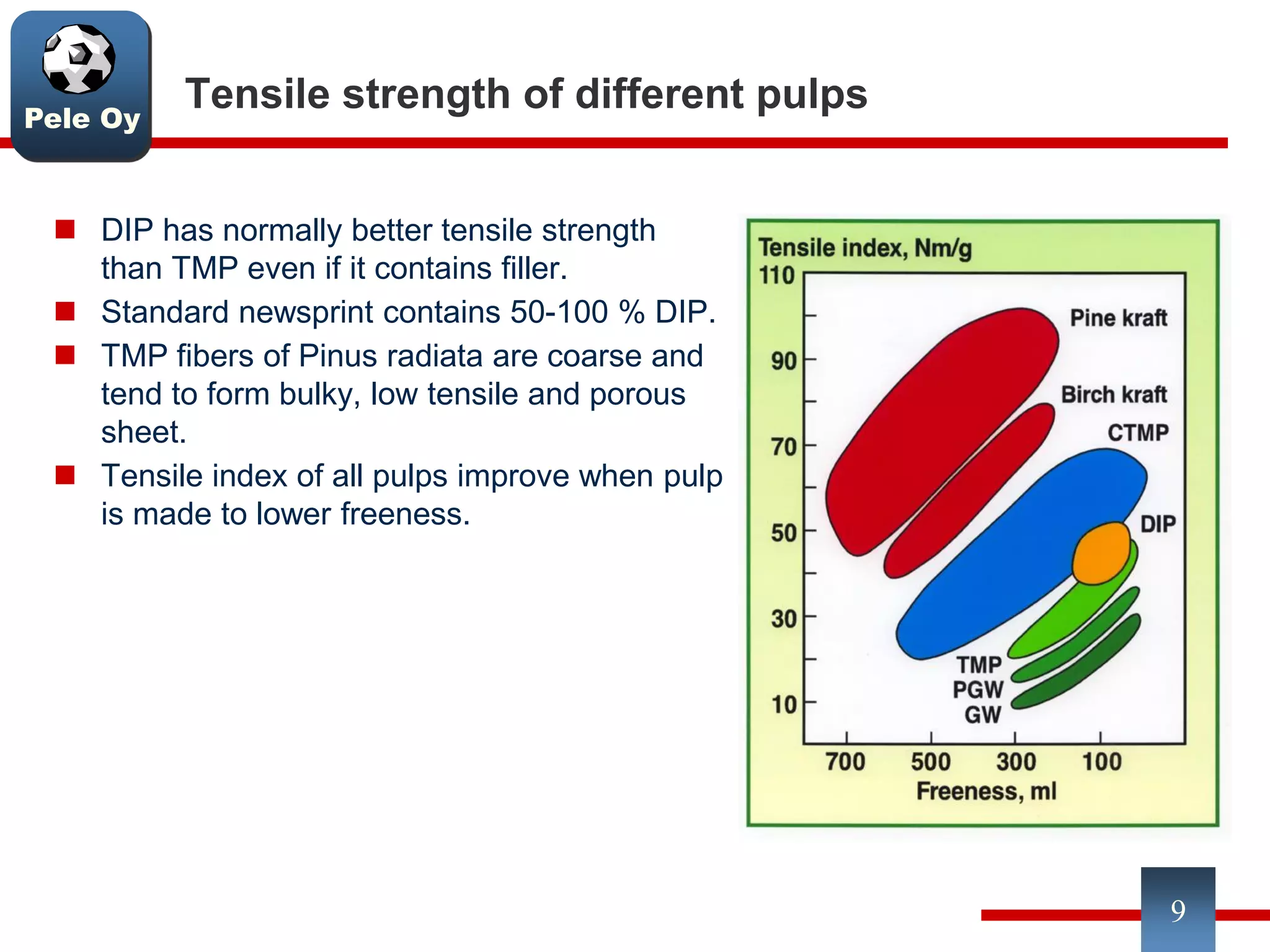
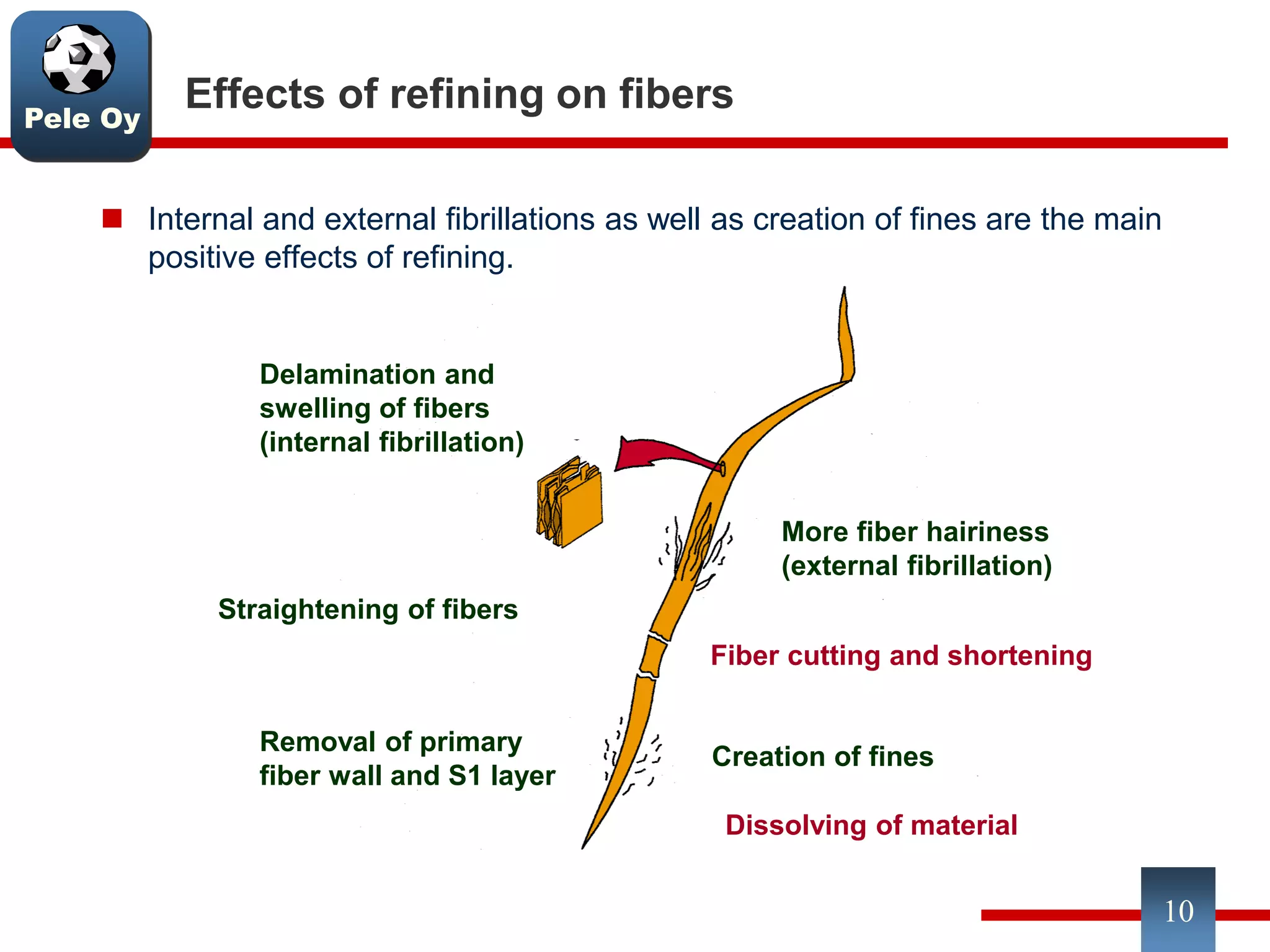
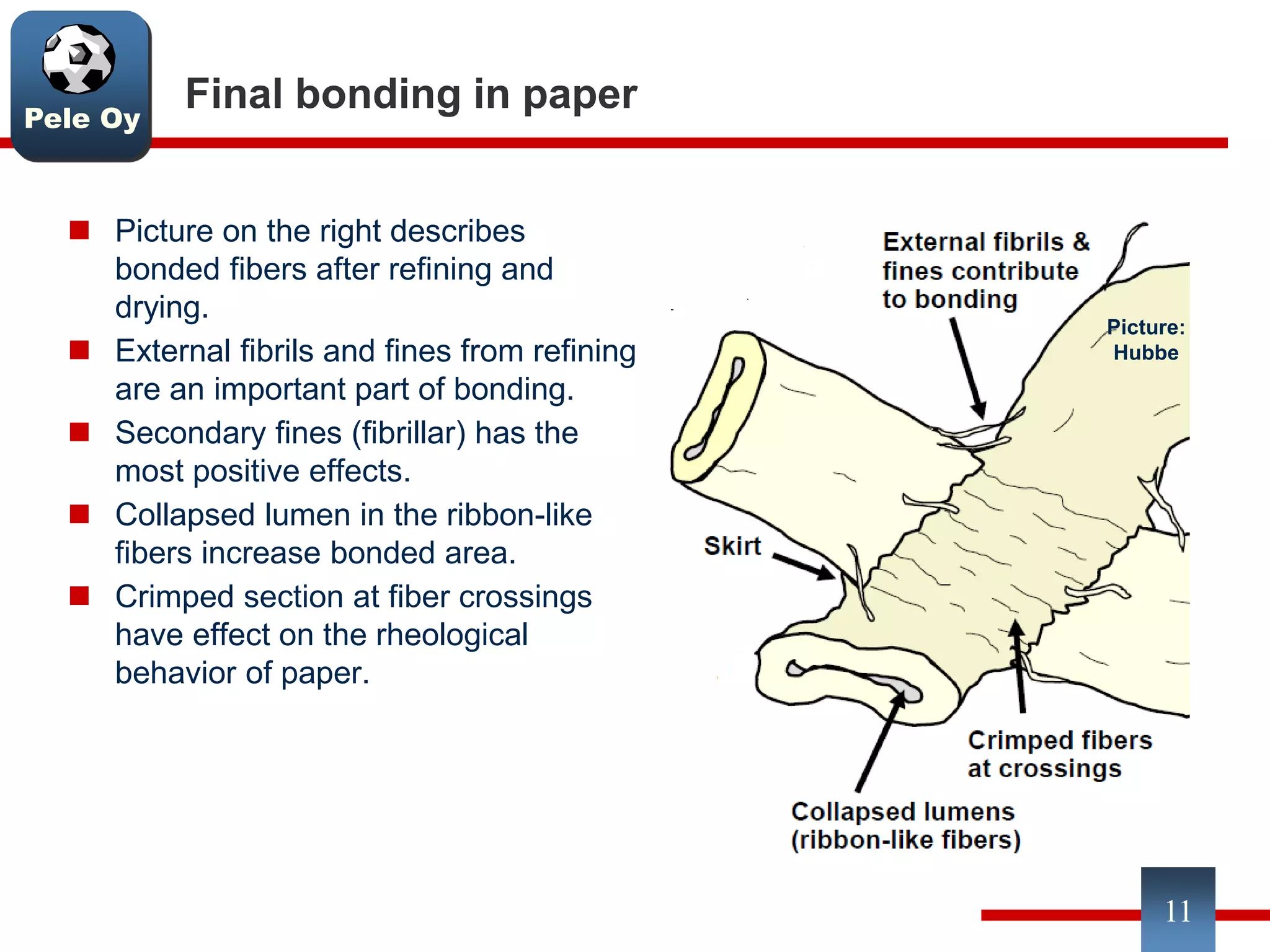
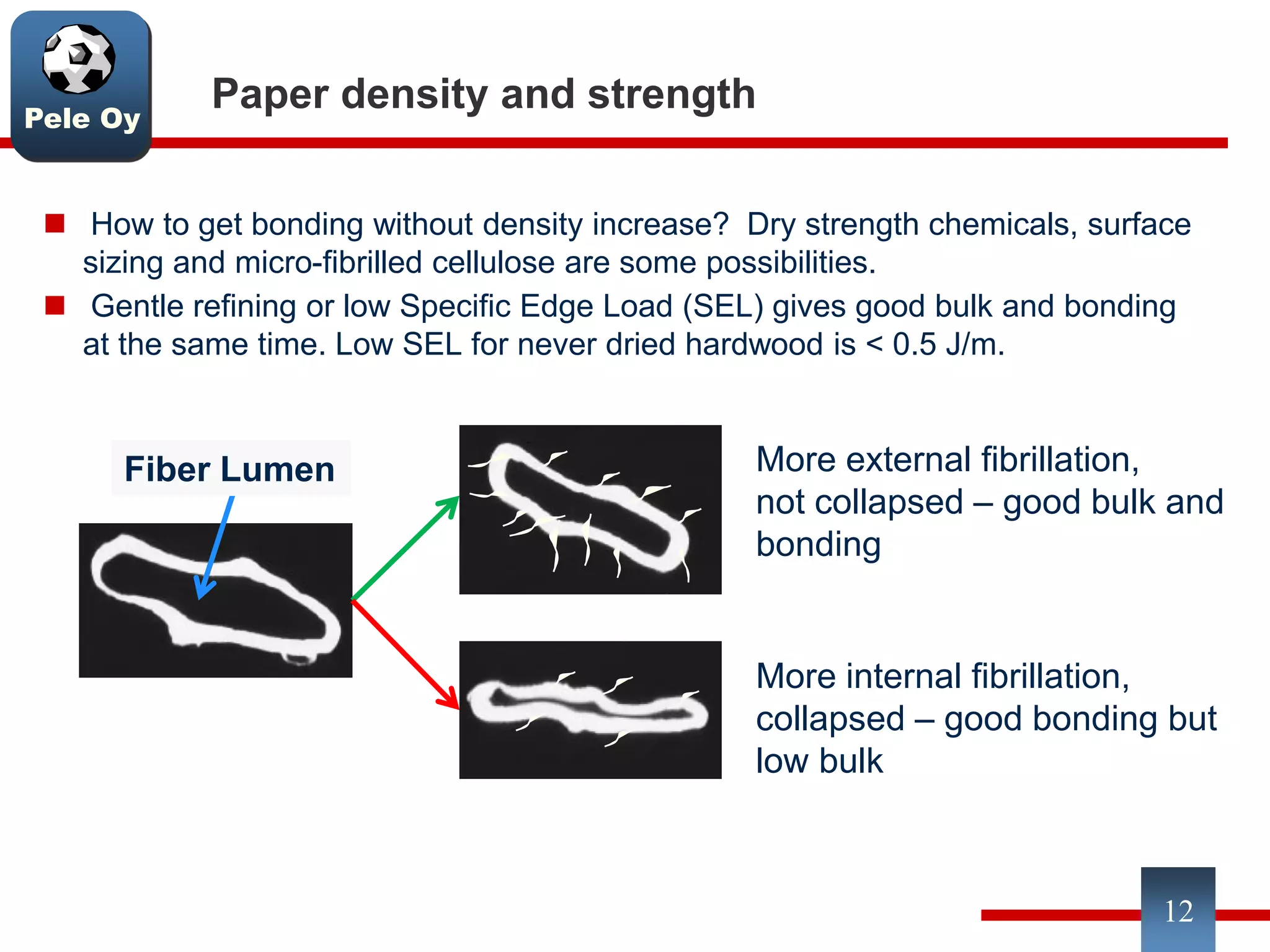
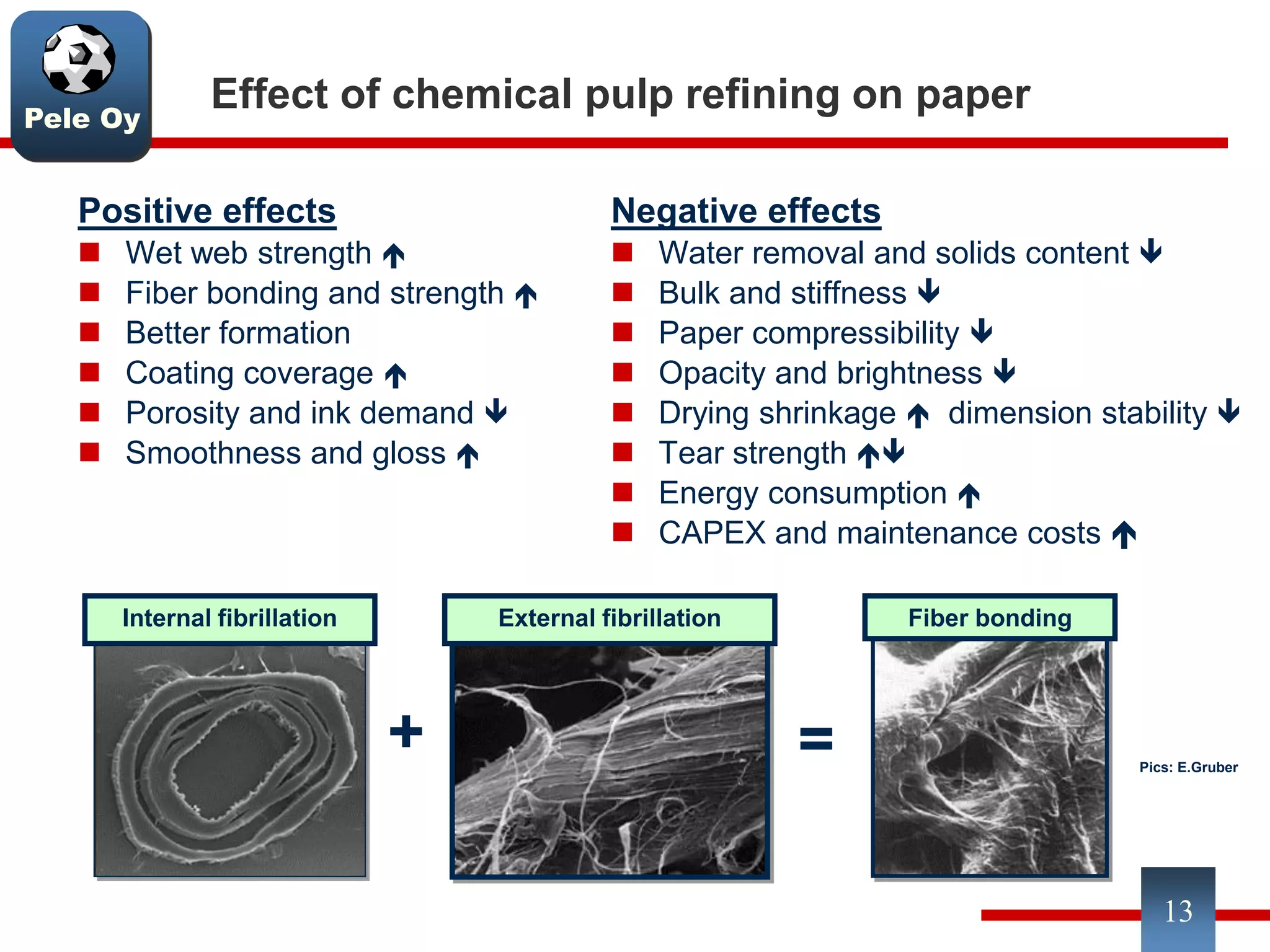
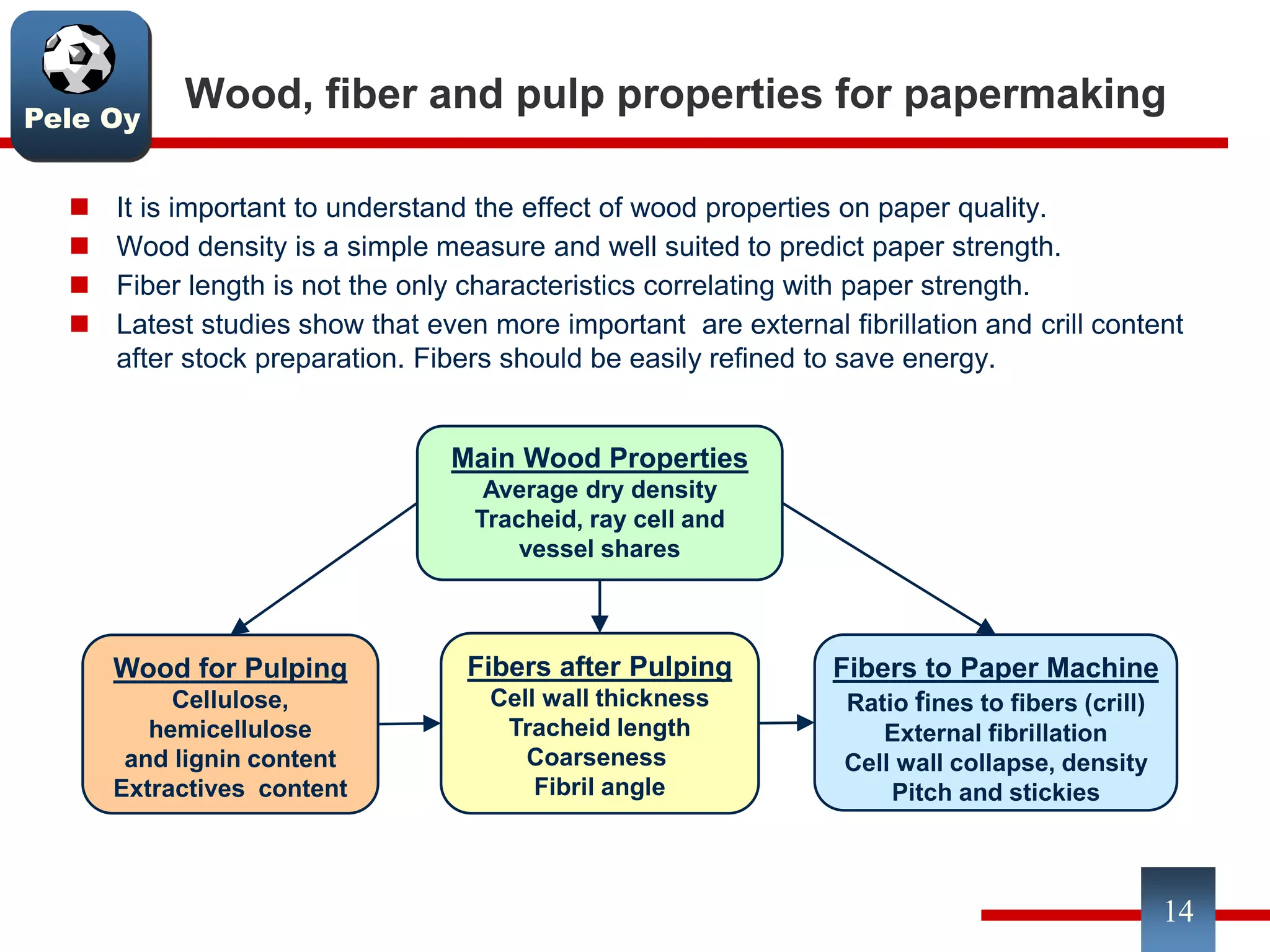
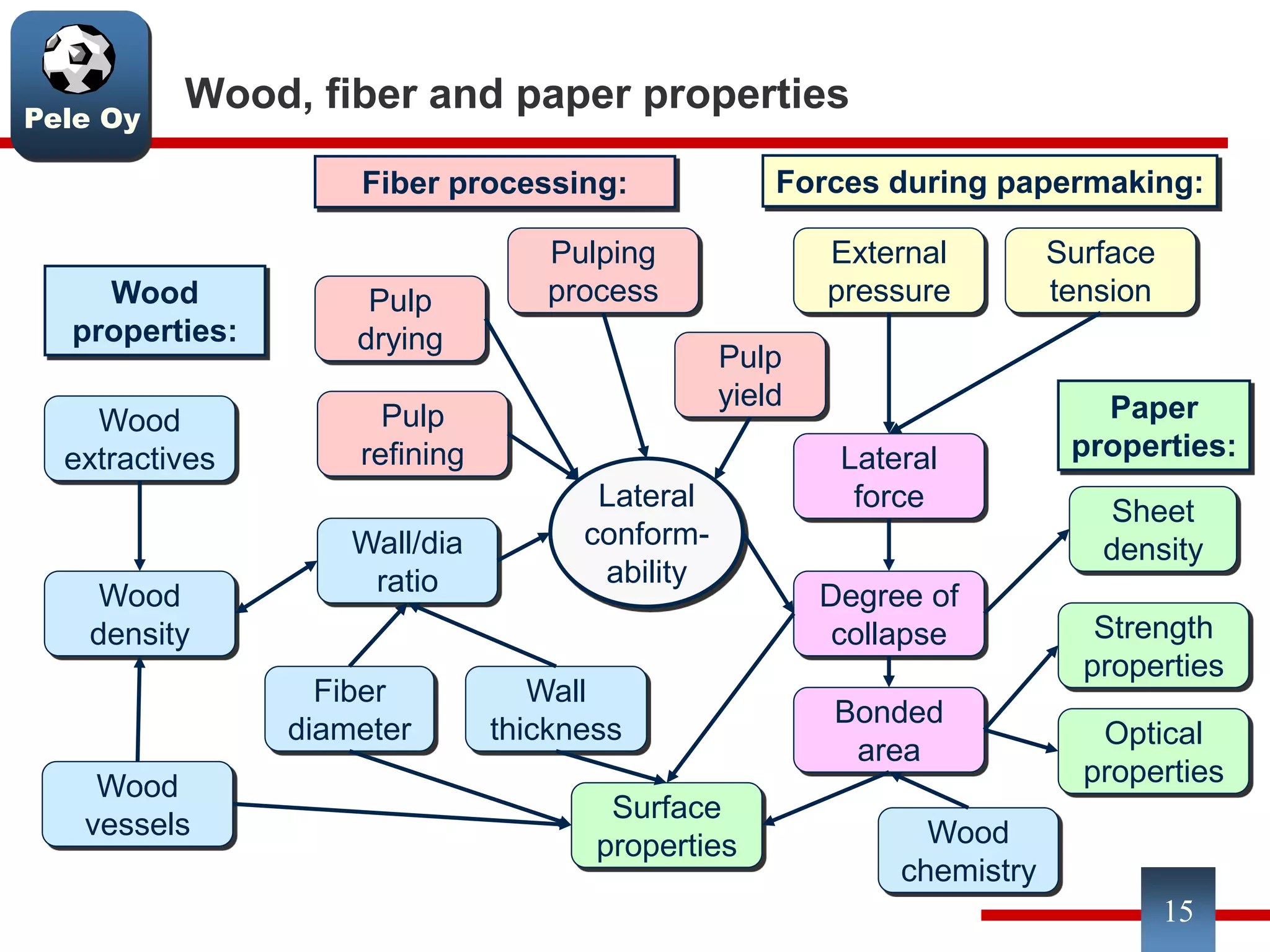
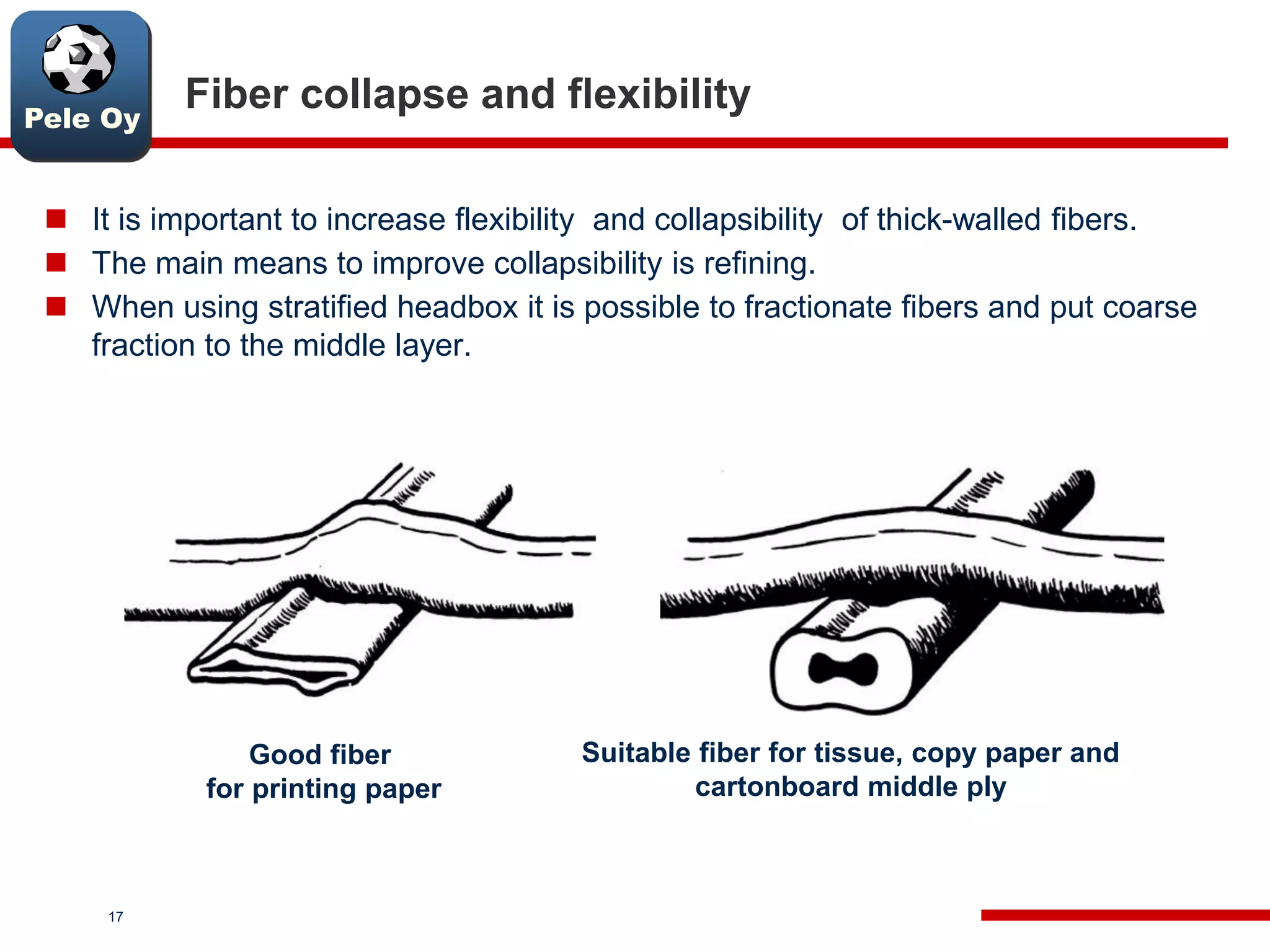
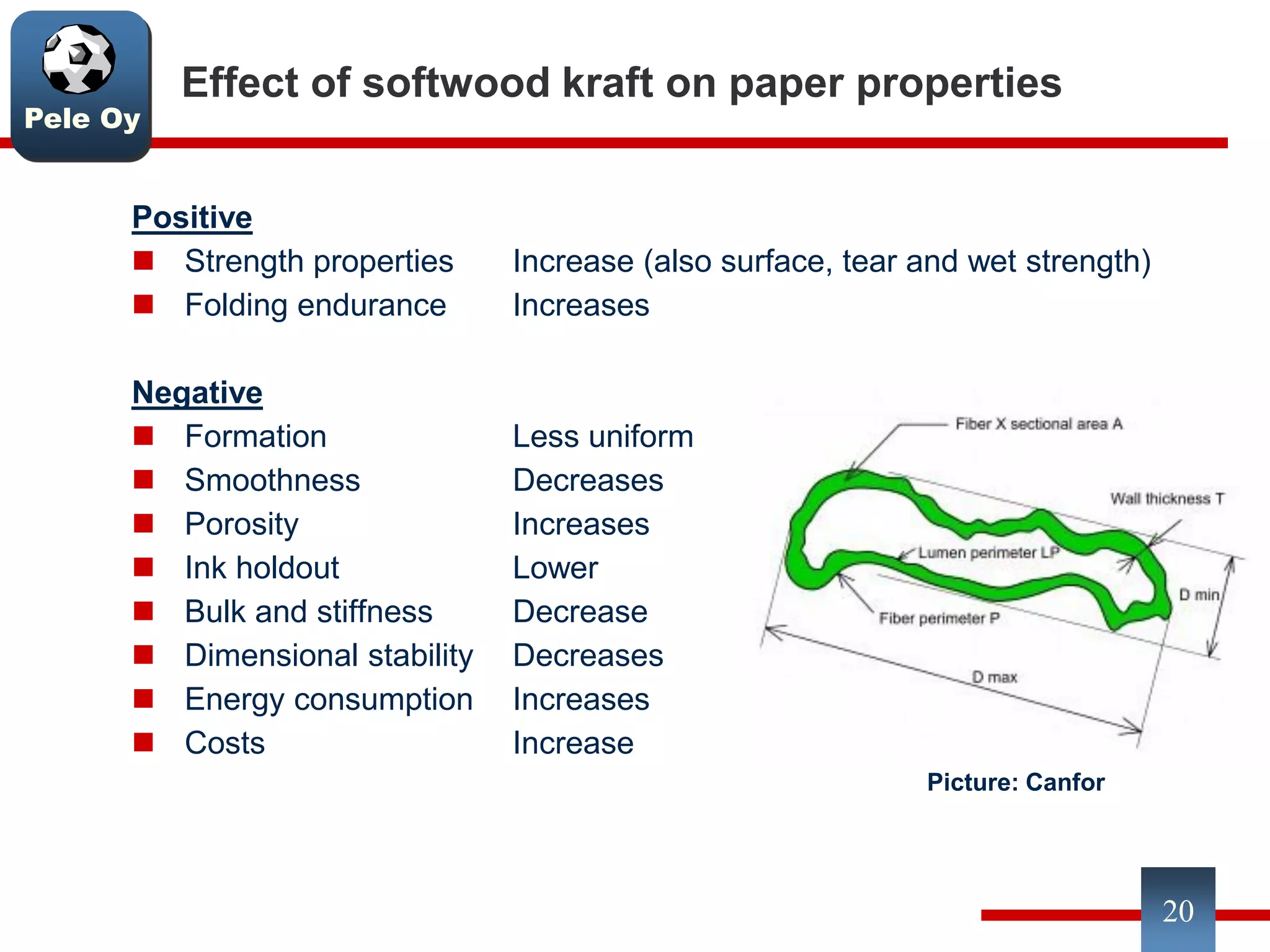
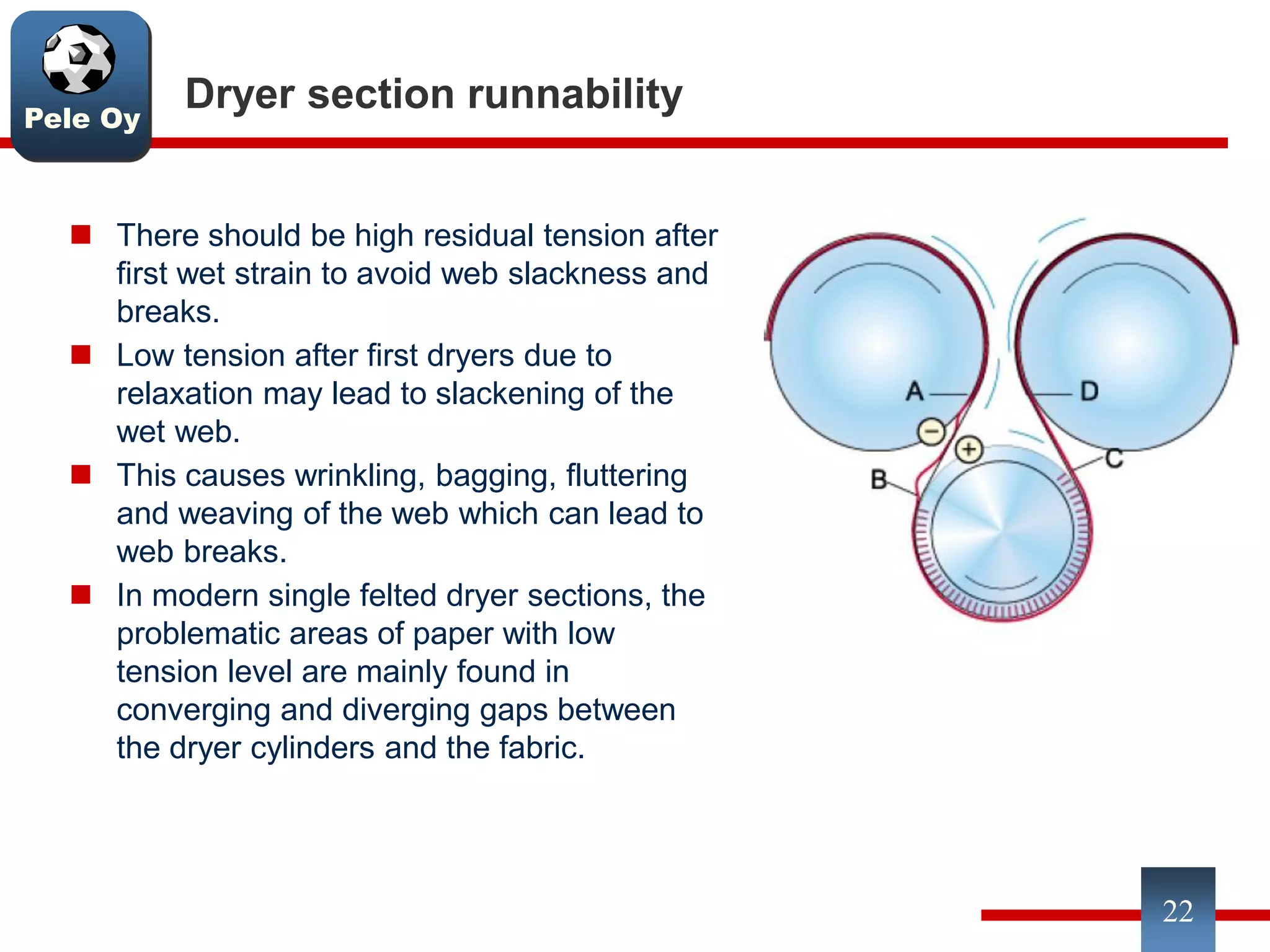
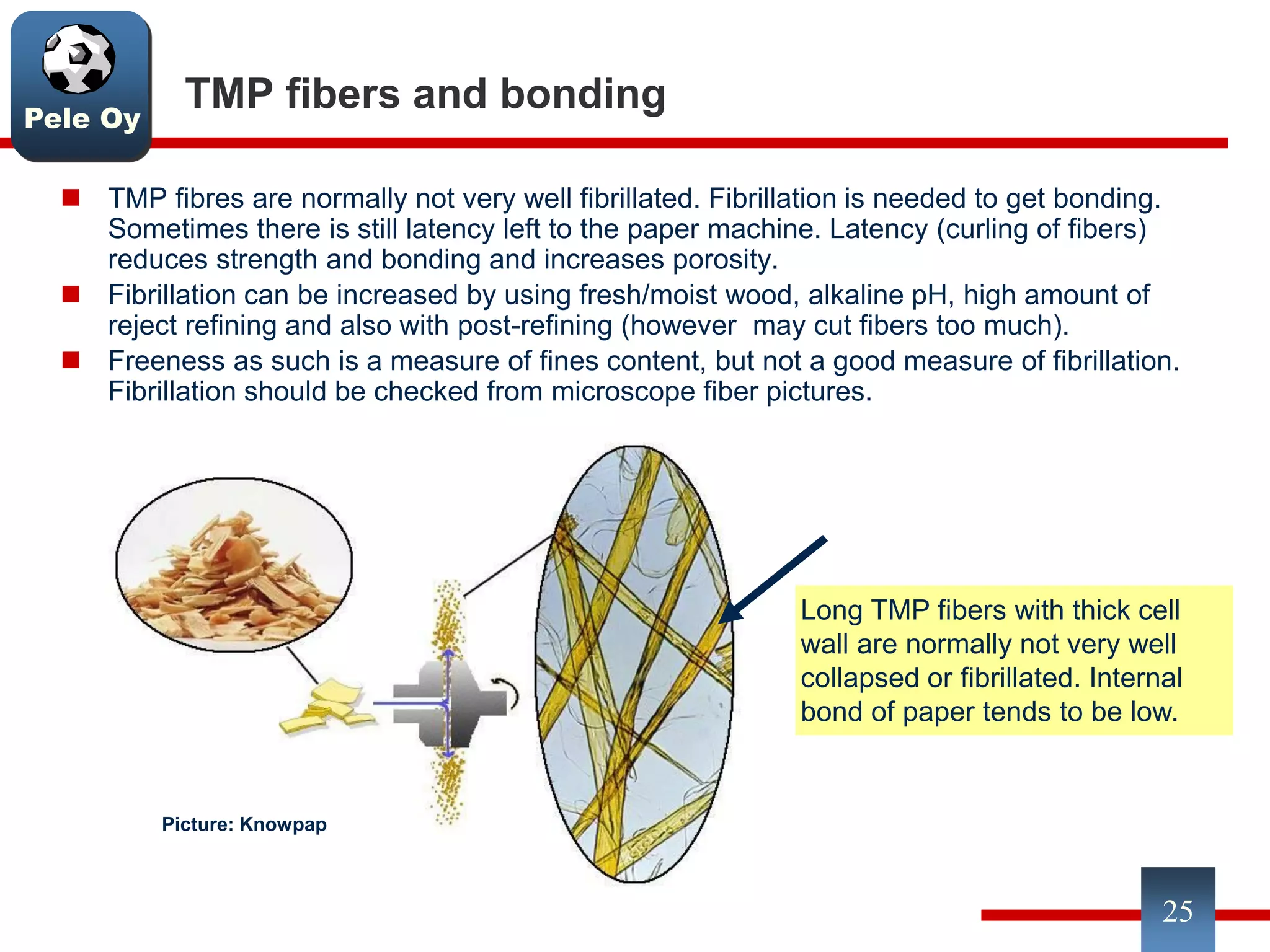
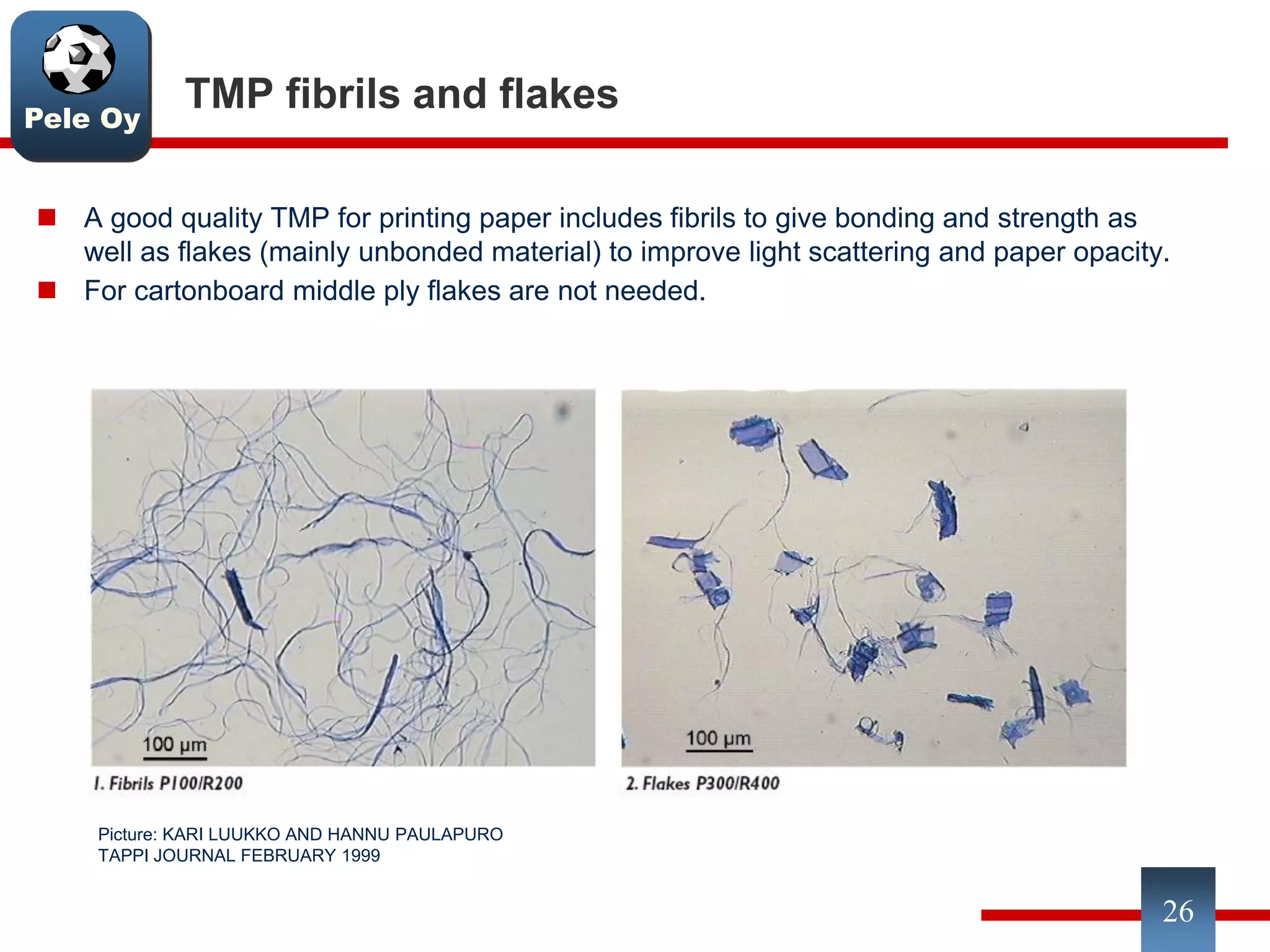
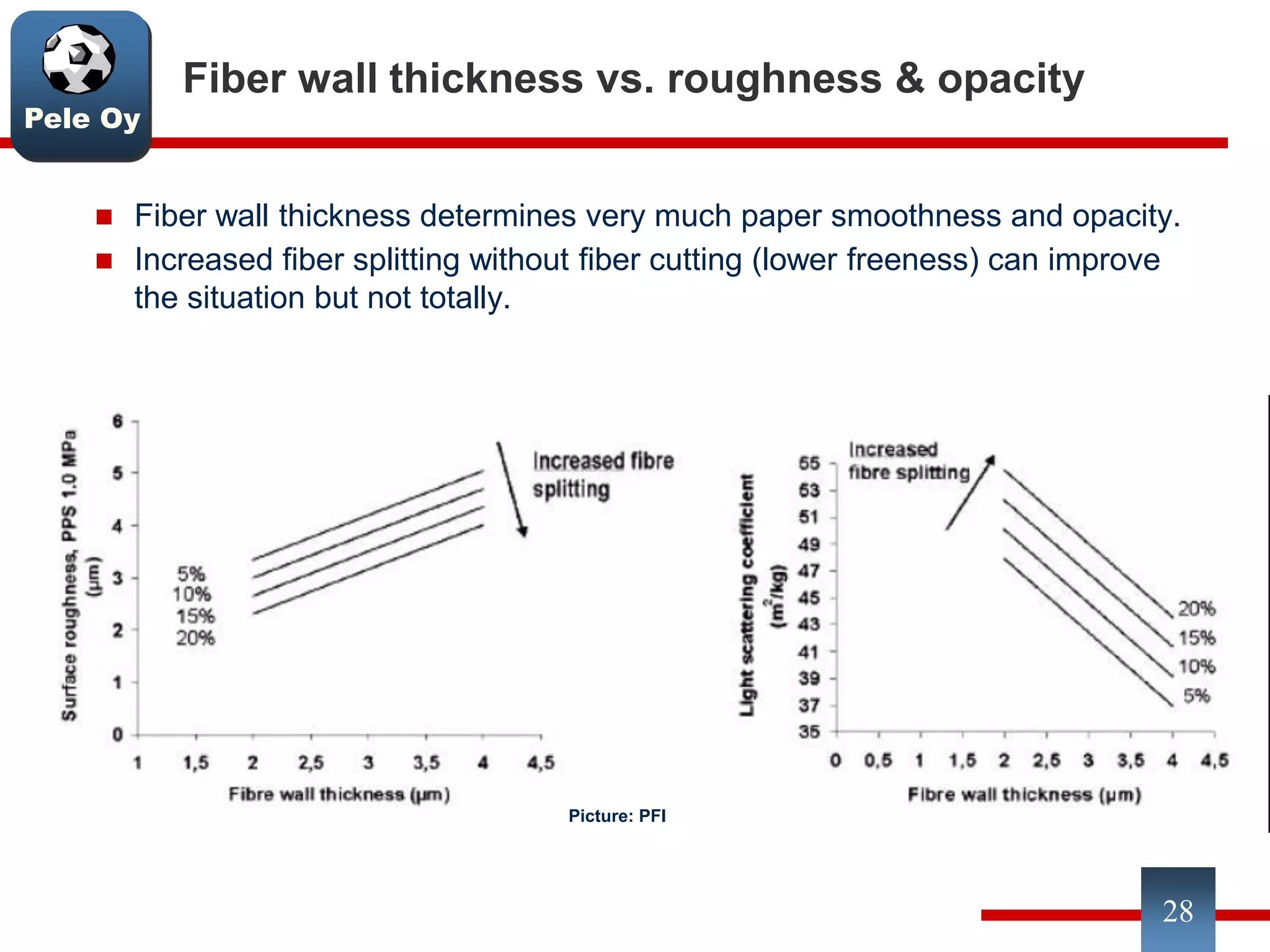
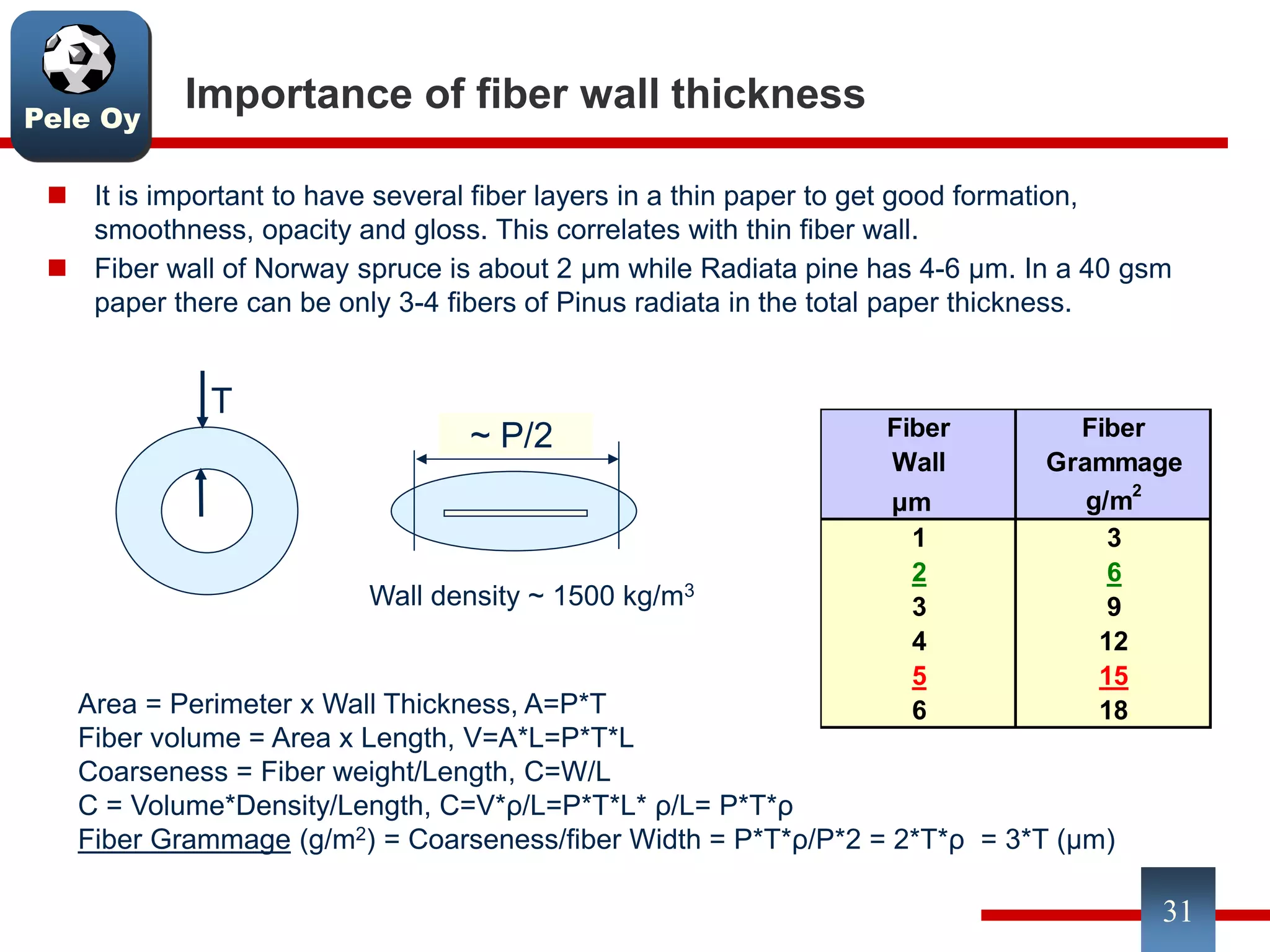
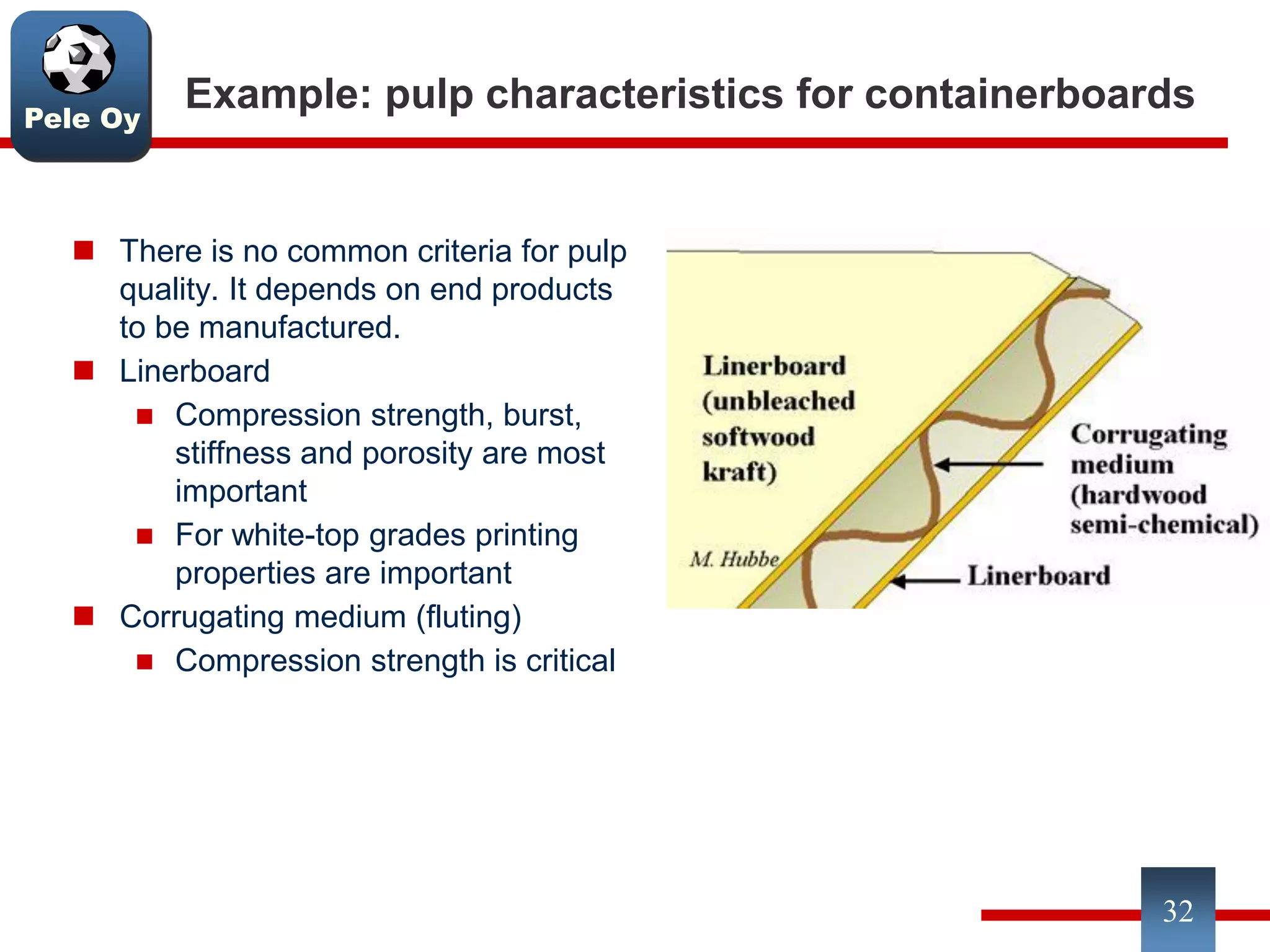
This document discusses differences between hardwood and softwood fibers used for papermaking. Hardwood fibers are shorter and thinner than softwood fibers. Softwoods contain mostly fibers (tracheids) which form the fiber network in paper, while hardwoods also contain vessel and ray cells which can cause issues. Fiber length, diameter, cell wall thickness and wood density impact paper properties like strength, bulk, and formation. The roles of different pulps, fillers and additives in achieving desired paper qualities are also reviewed. Optimal mechanical pulps for printing papers contain fibrillated fibers, fines, and few shives.