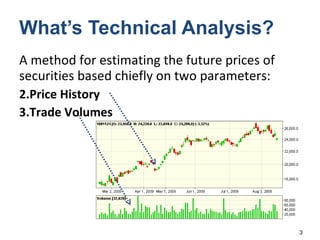
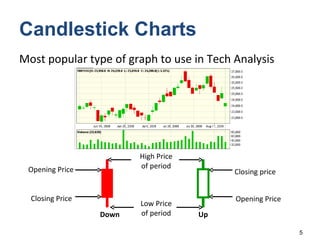
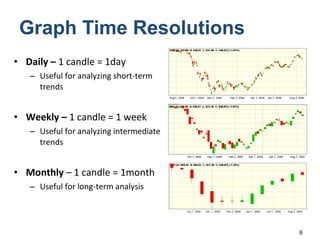
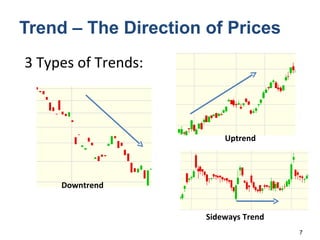
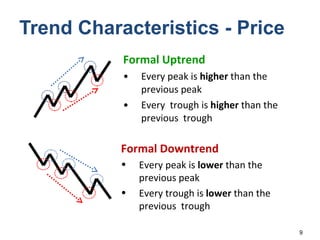
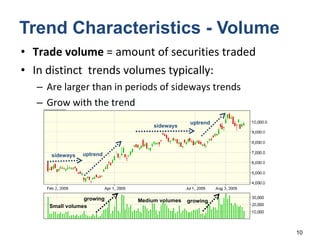
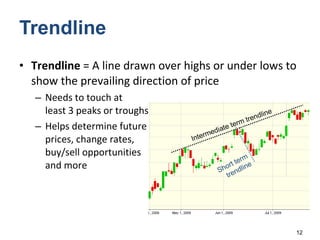
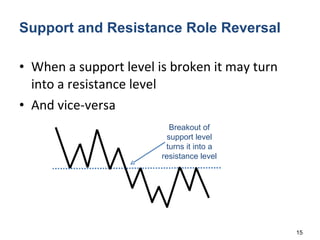
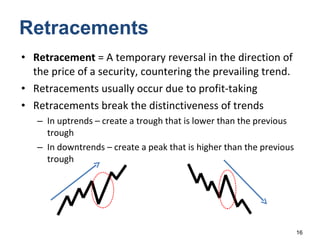
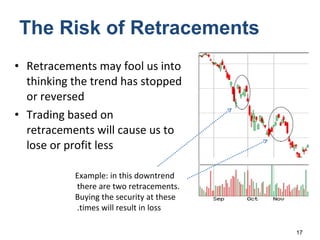
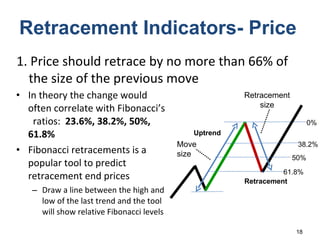
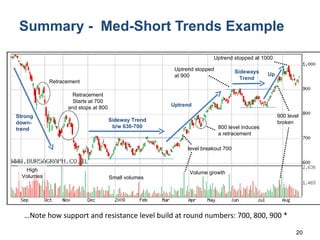
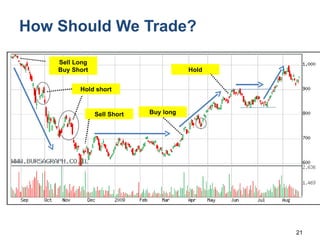
Technical analysis is a method for estimating future security prices based on historical price and volume data. It assumes market psychology repeats and that data can predict buyer and seller behavior. Charts like candlestick are used to analyze trends, support/resistance levels, and retracements. The golden rule is to trade with the prevailing trend: buy in uptrends, sell in downtrends, and avoid trading in sideways trends.