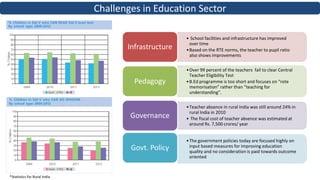
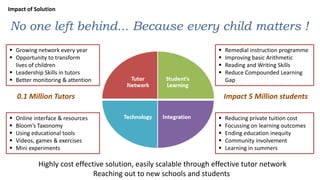
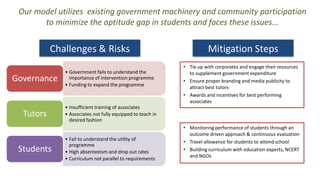
The document proposes a citizen-driven intervention program called "Stepping Stones" to bridge the learning gap among students in primary education in India by establishing a local network of citizen tutors who would provide supplemental remedial instruction to students during summer vacations using underutilized school infrastructure, with a focus on improving foundational skills in math, English, and other subjects through differential grading and targeted learning exercises. The program aims to be scalable, outcome-driven, and cost-effective by leveraging community participation and existing resources.