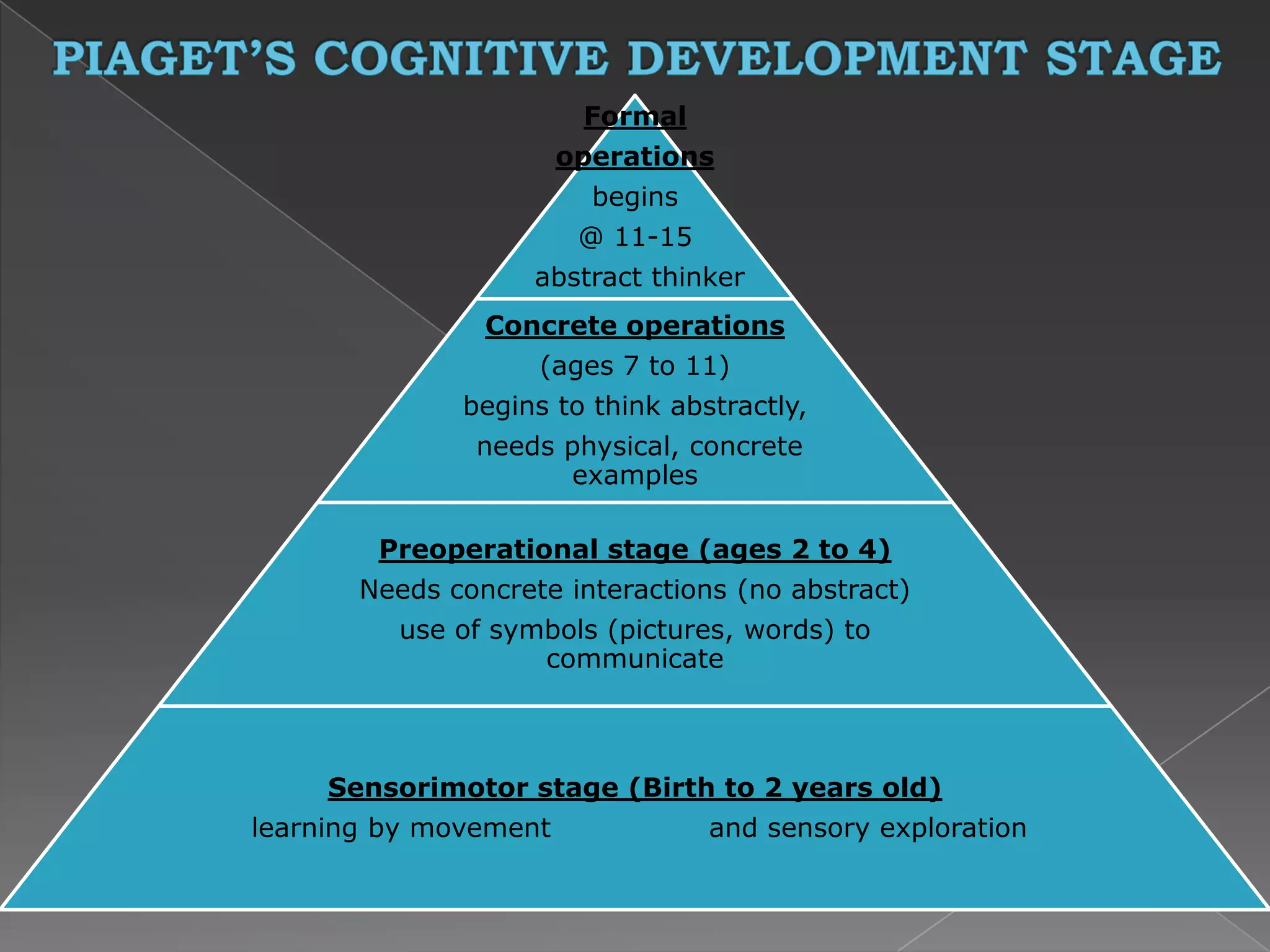
This document discusses behavioral and cognitive approaches to psychology and their implications for education. It describes key theorists in each approach, including Thorndike, Pavlov, Skinner, Bandura, and Gagne for behaviorism, and Montessori, Piaget, and Vygotsky for cognitivism. Behaviorism focuses on observable stimulus-response relationships and conditioning techniques, while cognitivism emphasizes internal mental processes like memory, perception, and stages of cognitive development. Both approaches aim to understand learning and inform curriculum design but differ in their views of the learner and role of environment.