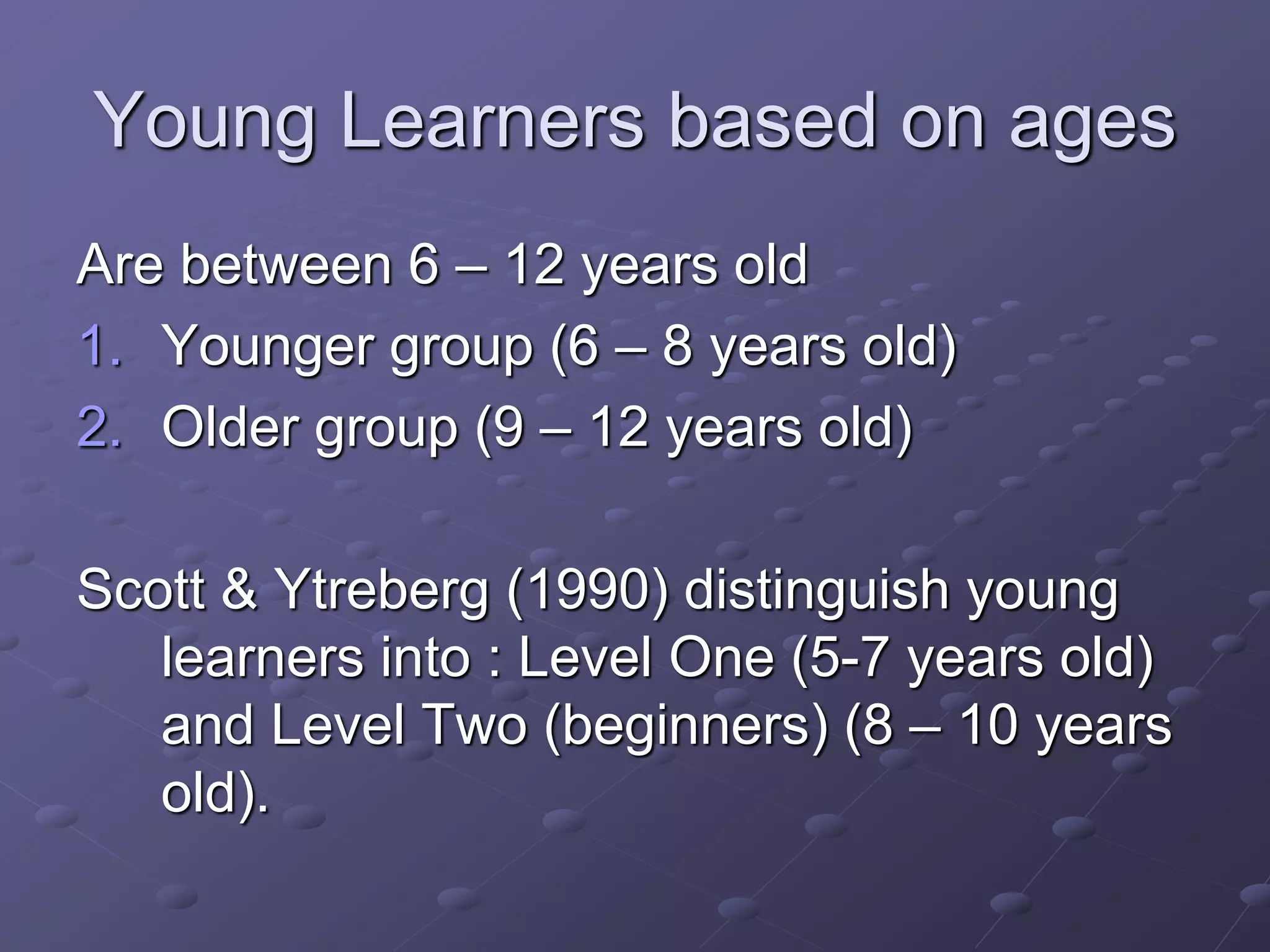
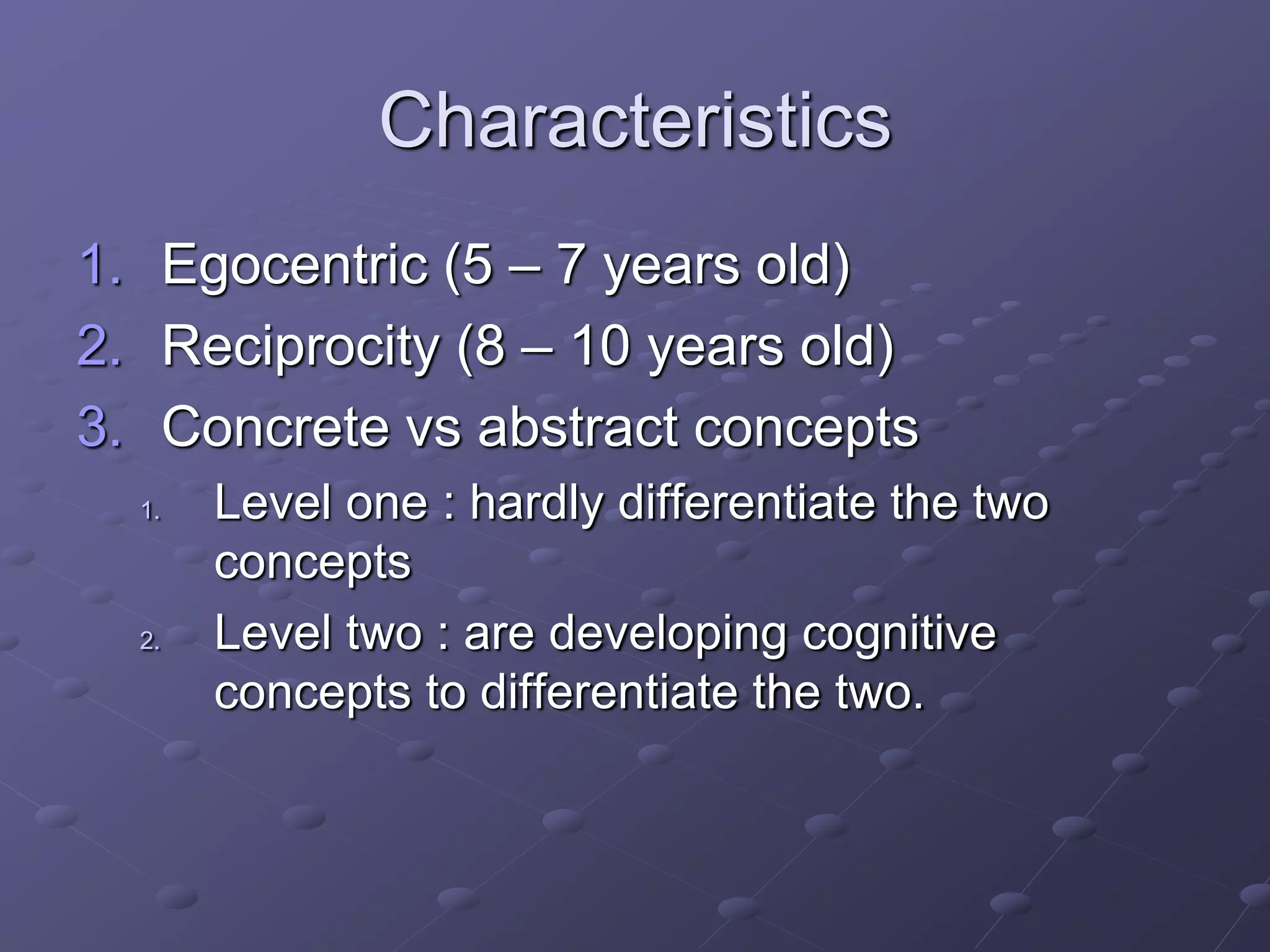
The document discusses teaching English to young learners between the ages of 6-12. It notes that children are generally better language learners than adults, especially between the ages of 2-10 according to the Critical Period Hypothesis. Young learners are divided into younger (ages 6-8) and older (ages 9-12) groups, with different characteristics for each. Effective teaching of young learners should be fun, natural, multi-sensory, concrete, and build on their existing knowledge by adding new concepts or experiences gradually.