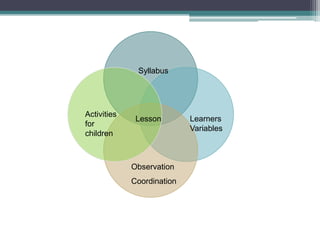
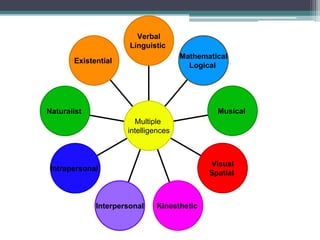
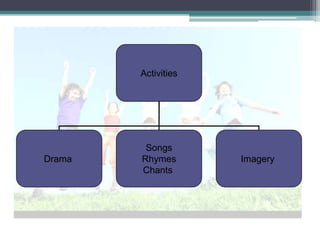
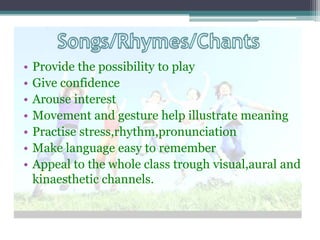
This document discusses learner variables and teaching strategies for children and adults learning English as a second language. It covers intellectual, sensory, and affective factors to consider for children, including the need for meaningful language, varied activities, and appealing to multiple intelligences. Teaching strategies like songs, rhymes, drama, and imagery are recommended. Guidance is provided on using activities, maintaining a supportive climate, and allowing mistakes. Differences between primary and secondary school contexts are also outlined.