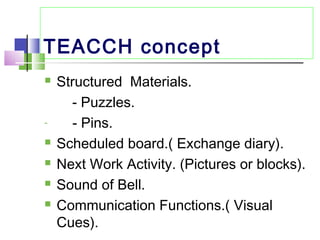
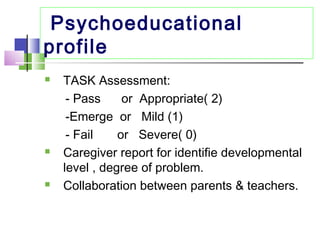
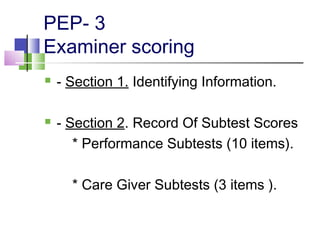
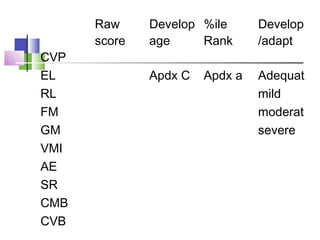
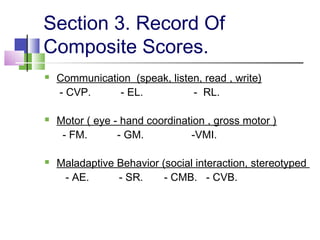
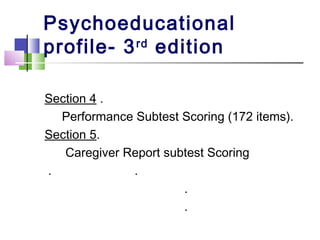
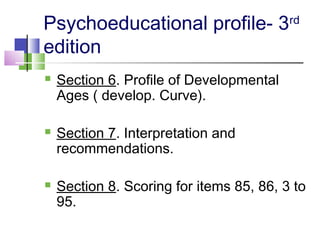
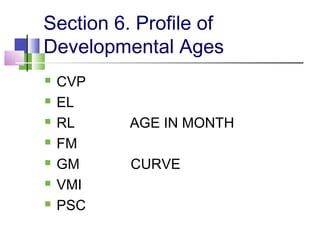
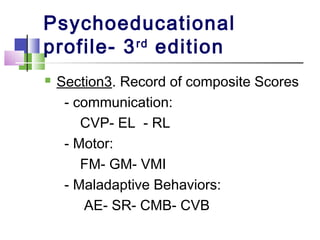
The TEACCH program aims to help people with autism live and work more effectively through structured teaching methods. It was established in 1966 as part of the University of North Carolina and provides diagnosis, individualized education programs, social skills training, and parent training. The TEACCH method emphasizes a structured physical environment, scheduled activities, and visual cues to improve skills and modify environments to accommodate needs. It uses the Psychoeducational Profile to assess developmental abilities and behaviors through performance tests and caregiver reports to develop individualized plans.