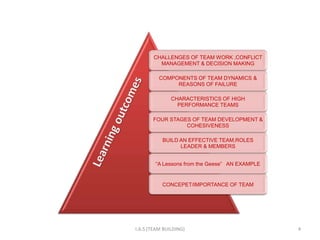
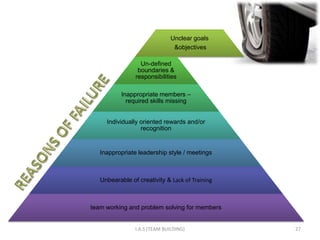
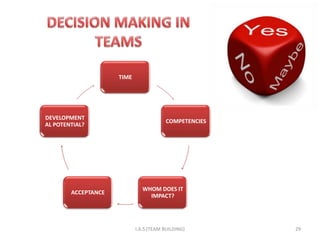
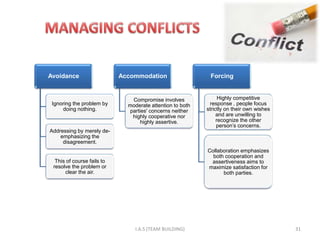
1. The document discusses challenges of teamwork such as conflict management and decision making. It covers components of team dynamics and reasons for team failure.
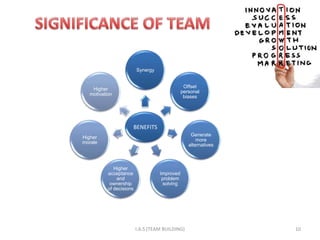
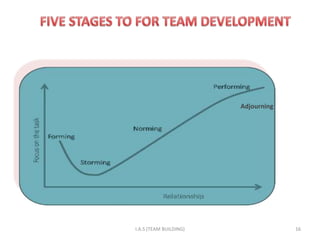
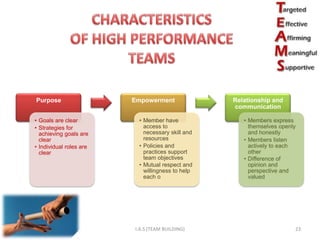
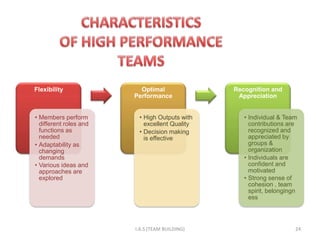
2. High-performing teams have clear goals and roles, effective communication, and recognize individual and team contributions. The four stages of team development are forming, storming, norming, and performing.
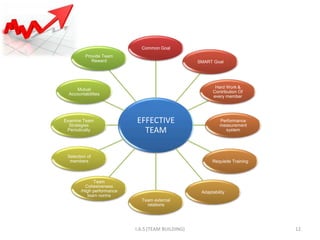
3. Building an effective team requires selecting members with complementary skills, establishing common goals and mutual accountability. Leaders must facilitate participation and manage conflict to foster cooperation.