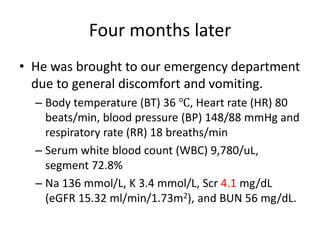
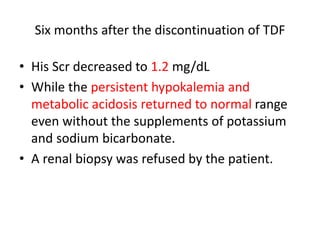
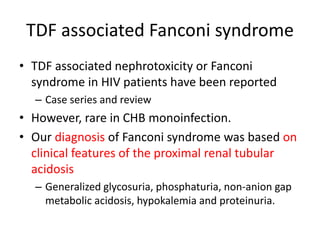
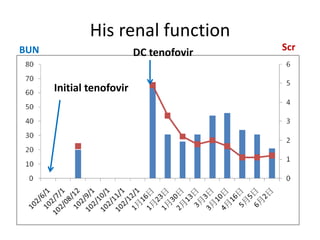
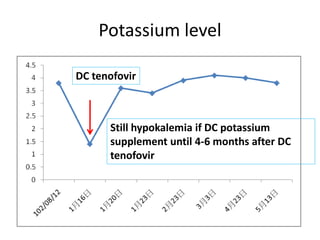
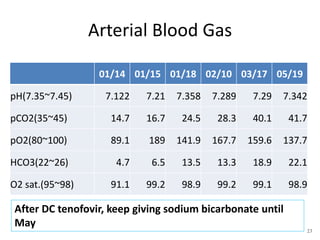
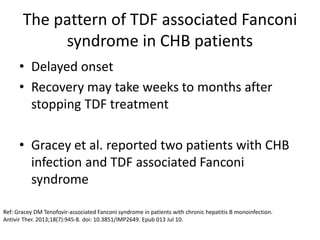
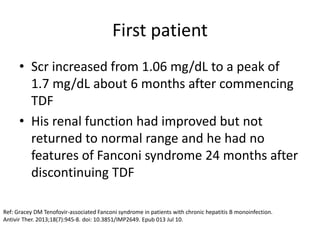
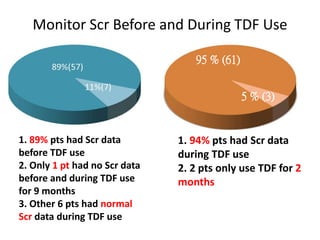
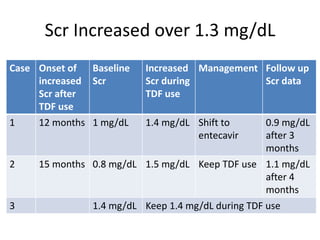
This case report describes a 72-year-old man with chronic hepatitis B who developed suspected tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-associated Fanconi syndrome. The man was treated with TDF and entecavir for hepatitis B. Over four months his renal function declined, and he developed hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis, and acute kidney injury. All features improved after discontinuing TDF, supporting the diagnosis of TDF-associated Fanconi syndrome. The report reviews the mechanism and risk factors of TDF nephrotoxicity and recommends monitoring renal function in patients taking TDF.



![Introduction
• Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)
– A nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and
chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection
• Side effects
– diarrhea (16%), asthenia (11%) and nausea (11%)
• Renal toxicity has been reported in HIV
infected patients, but rare in CHB infection
Ref: Viread (tenofovir) [package insert]. Foster City, CA: Gilead Sciences Inc; October 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tdffanconisyndrome20141122-151221024322/85/TDF-associated-Fanconi-syndrome-4-320.jpg)