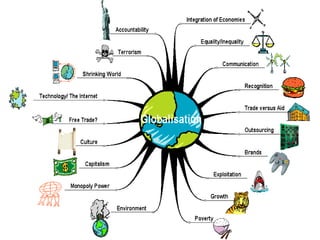
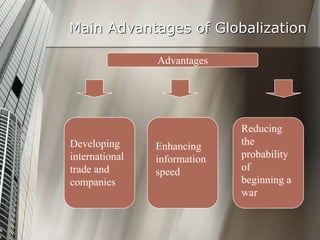
Globalization is a process of increasing economic, political, and cultural integration between countries through expanding corporate institutions and capitalist philosophies. It involves many countries and large multinational enterprises operating across borders. Globalization can be defined narrowly in economic terms or more broadly to include social and cultural aspects. While it offers some benefits like increased trade and information sharing, it also has disadvantages such as job losses and greater environmental pollution that require oversight.