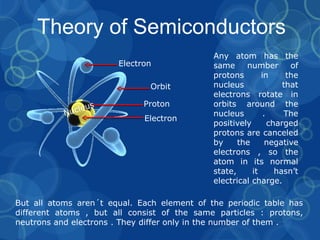
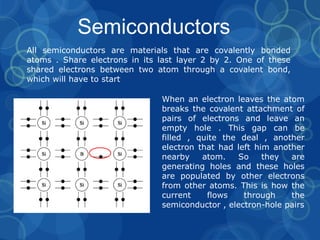
Semiconductors are materials that conduct electricity under certain conditions, lying between conductors and insulators. They are widely used in electronics like microprocessors, transistors, and any computerized or radio-using devices. Semiconductors are made of covalently bonded atoms that share electrons. When an electron leaves its atom, it creates an "hole" that can be filled by another electron, generating electron-hole pairs that allow electric current to flow through the semiconductor material. The most common semiconductor materials are silicon and germanium. Semiconductors can be classified as intrinsic, with virtually no impurities, or extrinsic, which are doped with impurities to have extra electrons or holes that enhance conductivity.