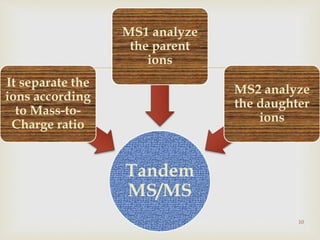
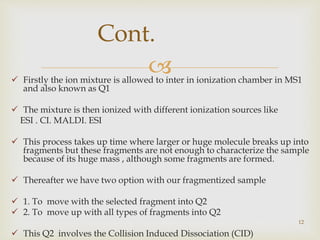
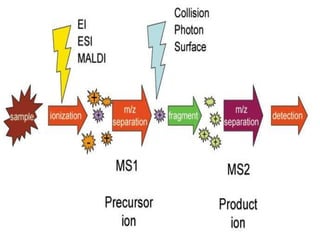
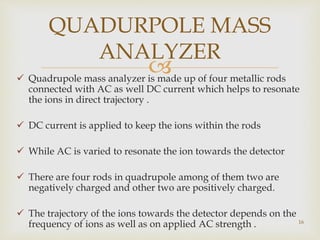
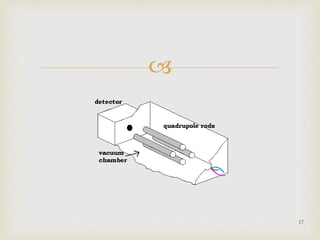
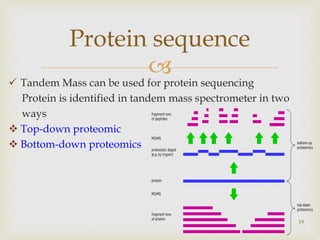
Tandem mass spectrometry is a technique that uses multiple stages of mass spectrometry to analyze molecular ions and their fragmentation patterns. It works by first analyzing parent ions (MS1), then inducing fragmentation through collision with gas molecules to produce daughter ions, which are then analyzed (MS2). This allows for more detailed structural information to be obtained compared to single-stage mass spectrometry. Common applications include protein sequencing, DNA/RNA sequencing, and newborn screening for metabolic diseases.