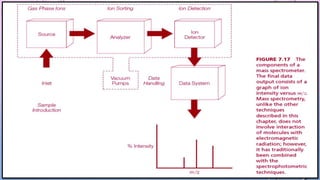
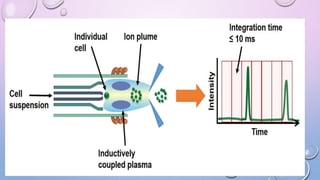
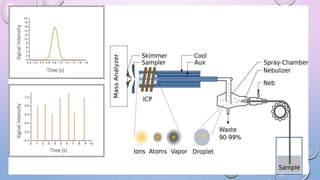
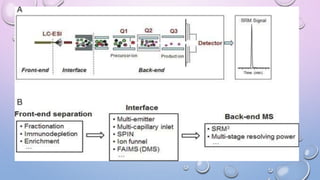
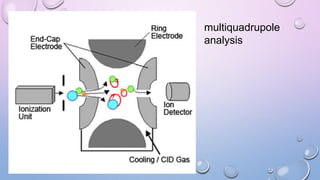
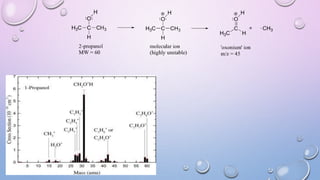
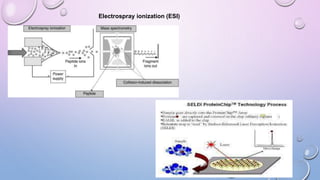
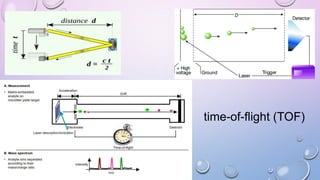
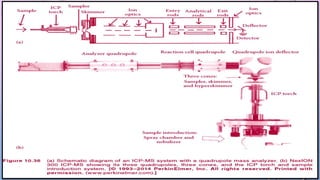
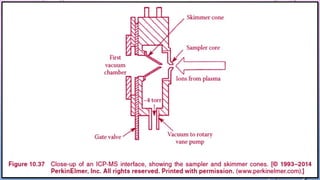
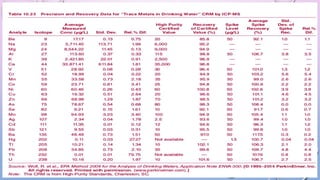
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) allows for analysis of elements at very low concentrations. It works by ionizing analyte atoms from liquid samples using plasma and then detecting the resulting ions using a mass spectrometer. ICP-MS provides high sensitivity, accuracy, and a wide linear dynamic range. It has numerous applications including environmental analysis, clinical analysis, and analysis of geological and metallurgical samples. The key components are the inductively coupled plasma ion source, interface between the plasma and mass spectrometer, quadrupole or time-of-flight mass analyzer, and detector.