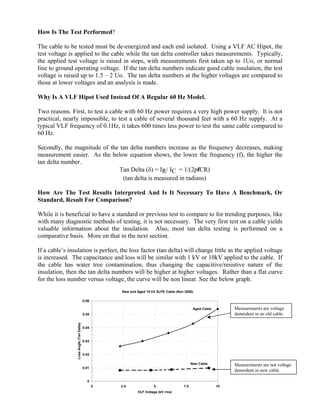
Tan δ (delta) testing measures the dissipation factor of cable insulation to determine quality and predict remaining life. It works by applying a very low frequency AC voltage and measuring the phase shift between the voltage and current, which indicates the ratio of resistive to capacitive current through the insulation. Higher phase shift angles mean more defects in the insulation. While no set standards exist, utilities can use comparative tan δ testing over time to prioritize cable replacement. The test is inexpensive, easy to perform, and can evaluate long cable runs using specialized very low frequency AC hipots.