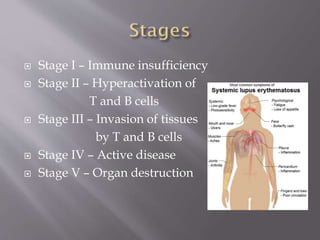
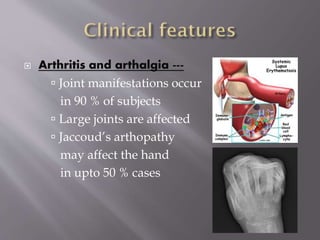
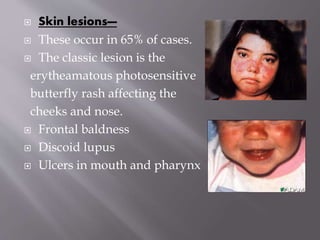
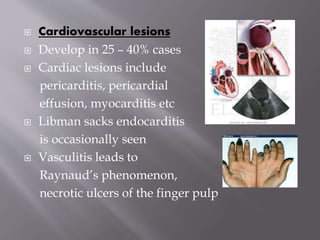
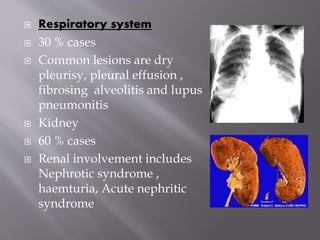
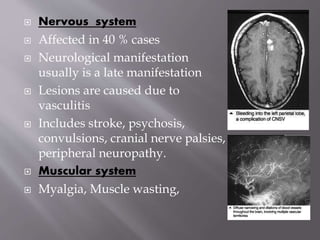
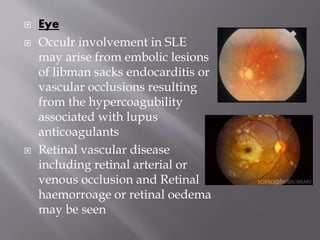
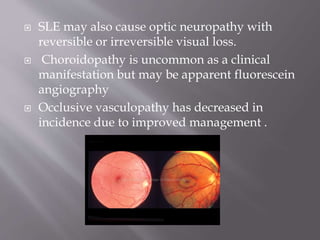
This document provides an overview of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), including its classification, causes, symptoms, and treatment. It notes that SLE can be systemic or discoid and is caused by autoantibodies that result in tissue damage through type II and III hypersensitivities. Common symptoms involve the joints, skin, cardiovascular, respiratory, kidney, nervous and muscular systems. Treatment depends on severity, ranging from NSAIDs and antimalarials for mild disease to high-dose corticosteroids, immunosuppressants or cytotoxic drugs for more serious symptoms affecting organs.