Embed presentation
Download to read offline




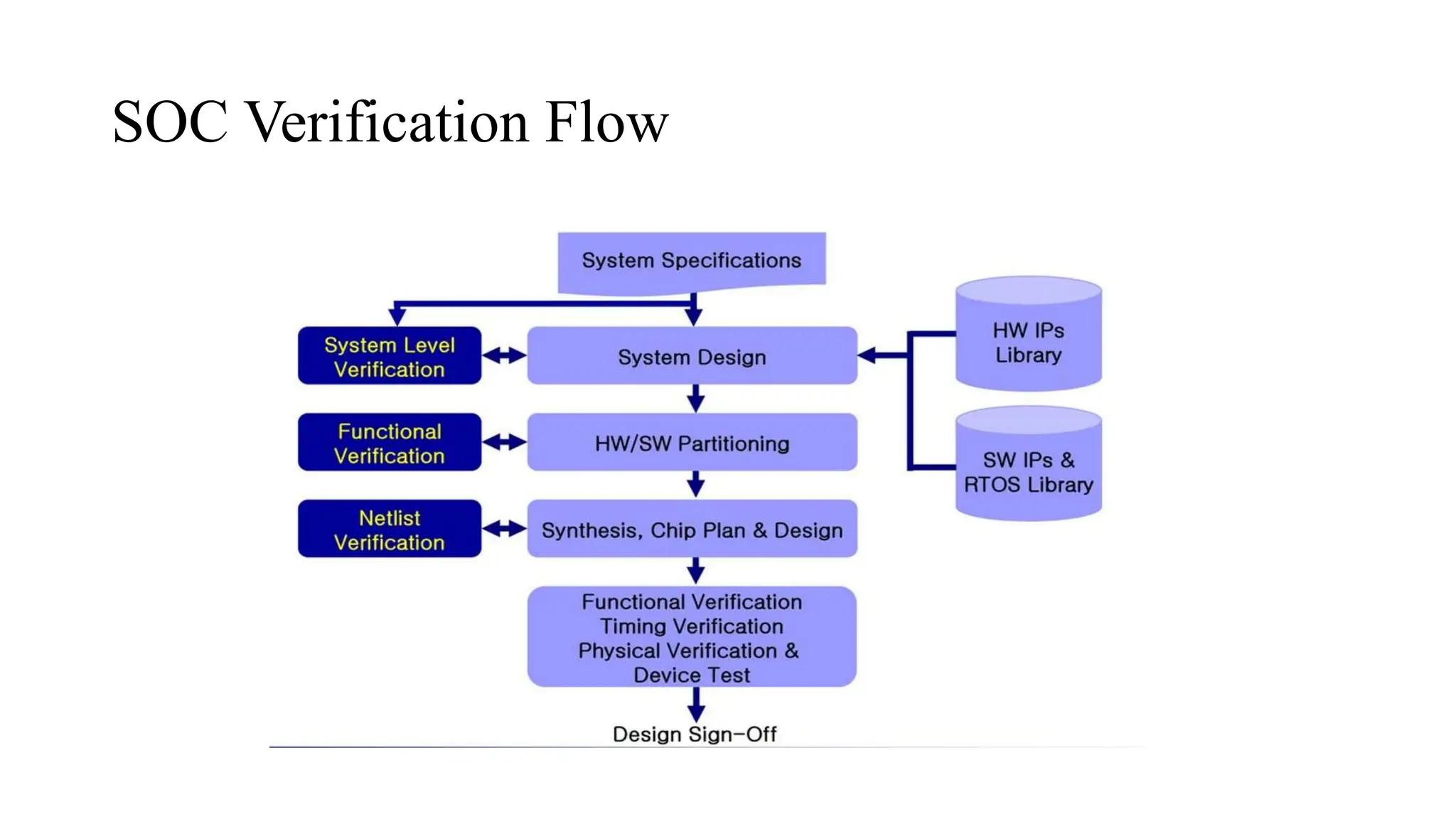


A SOC (System On Chip) is a microchip that integrates all or most components of an electronic system, such as a microcontroller, microprocessor, and several processor cores with peripherals like GPUs, WiFi, and cellular networks. SOCs aim to reduce power consumption, area, and cost while improving performance by minimizing latency, interface delays, and speeding up data transmission. They are used in embedded systems, mobile computing, and personal computers. SOC verification tests that a design meets specifications before production and must automate tests on embedded processors while increasing scope to check performance, power, safety, and security.








