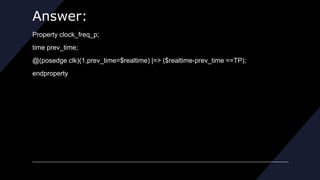
clock_freq_p;
time prev_time;
@(posedge clk)(1,prev_time=$realtime) |=> ($realtime-prev_time ==100ns);
endproperty
a: assert property(clock_freq_p);
This property checks if the clock is running at 10MHz by checking if the time between two positive edges is 100ns (period of a 10MHz clock). It uses $realtime to get the current simulation time and saves the previous time in prev_time. On every positive edge, it checks if the difference between current and previous time is 100ns.


![TYPES OF ASSERTION
IMMEDIATE ASSERTION
1] Immediate assertions check for a
condition at the zero/current simulation
time.
2]An immediate assertion is the same as
an if..else statement with assertion
control. Immediate assertions have to be
placed in a procedural block definition.
CONCURRENT ASSERTION
• 1] Concurrent assertions check the
sequence of events spread over
multiple clock cycles
• 2]The test expression is evaluated at
clock edges based on the sampled
values of the variables involved,it can
be placed in a procedural block,
a module, an interface or a
program definition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![Types cont..
• 3] syntax :
• label: assert(expression)
action_block;
Ex: always @(posedge clk) assert
(a && b);
• 3]syntax:
• c_assert: assert
property(@(posedge clk) not(a
&& b));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-5-320.jpg)

![IMPLECATION OPERATOR
1]Need of Implication Operator ??
sequence seq;
@(posedge clk) a ##2 b;
endsequence
2]TYPES OF IMPLICATION OPERATOR
A] OVERLAPPING IMPLICATION OPERATOR
B] NON-OVERLAPPING IMPLICATION OPERATOR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-7-320.jpg)









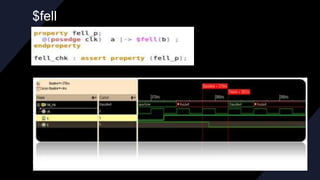

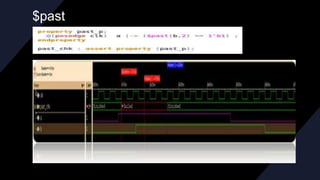

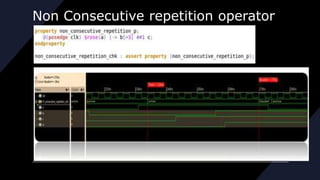
![REPETITION OPERATOR
1] Consecutive repetition operator
2] Go to repetition operator
3] Non Consecutive repetition operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![Consecutive repetition operator:
Signal_name1 [->n] ##1
signal_name2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-22-320.jpg)





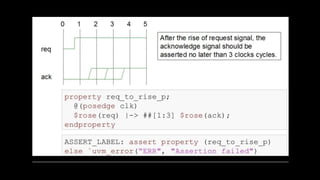
![Question:::
• 1] check if clock of given frequency is working fine or not.
.lets assume duty cycle as 50% ???
Or
Write a checker to see if clock is running at 10MHZ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assertion-230213112922-28bd0a74/85/assertion-pptx-29-320.jpg)