Embed presentation




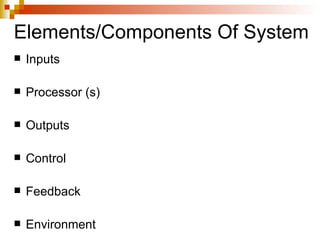
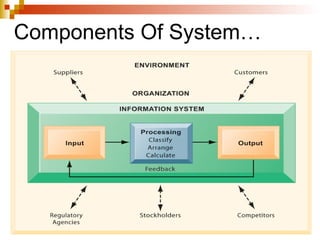



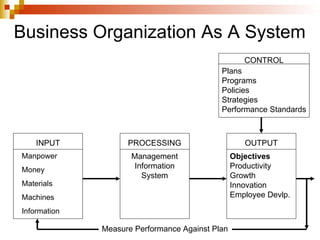

A system is defined as an orderly grouping of interdependent components linked together according to a plan to achieve a specific objective. Key aspects of a system include interrelationships and interdependence among components, and components including inputs, processors, outputs, and control/feedback. Systems can be conceptual or empirical, natural or manufactured, and have characteristics such as organization, interaction, central objective. The systems approach is used to build information systems and involves modeling a business organization as a system with inputs, processing, and outputs.









