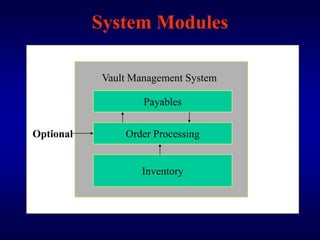
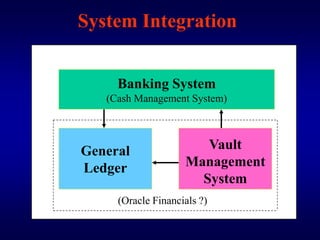
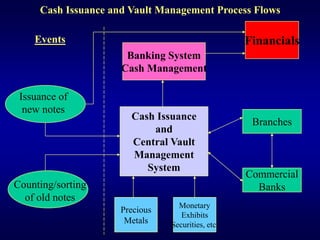
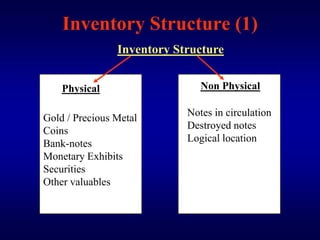
The document describes a vault management system for central banks that manages physical and non-physical inventories of assets like cash, precious metals, and securities. It integrates with Oracle applications and provides features for inventory, purchasing, order processing, and accounting integration. The system tracks items by organization, location, sub-inventory and includes security, reporting, and auditing capabilities.











![Transaction Set-Up
Transactions are managed by the Transaction
Manager in which are defined:
• Transaction types
• Transaction profile options (material transactions,
reservation, move transaction [work in process, importation of portable
bar code reader, etc.], resource cost transaction, etc.)
• Transaction reasons
• Control options
• Default locator and sub-inventory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vaultmanagementsystemforcentralbanks-120228232355-phpapp01/85/Vault-management-system_for_central_banks-16-320.jpg)








