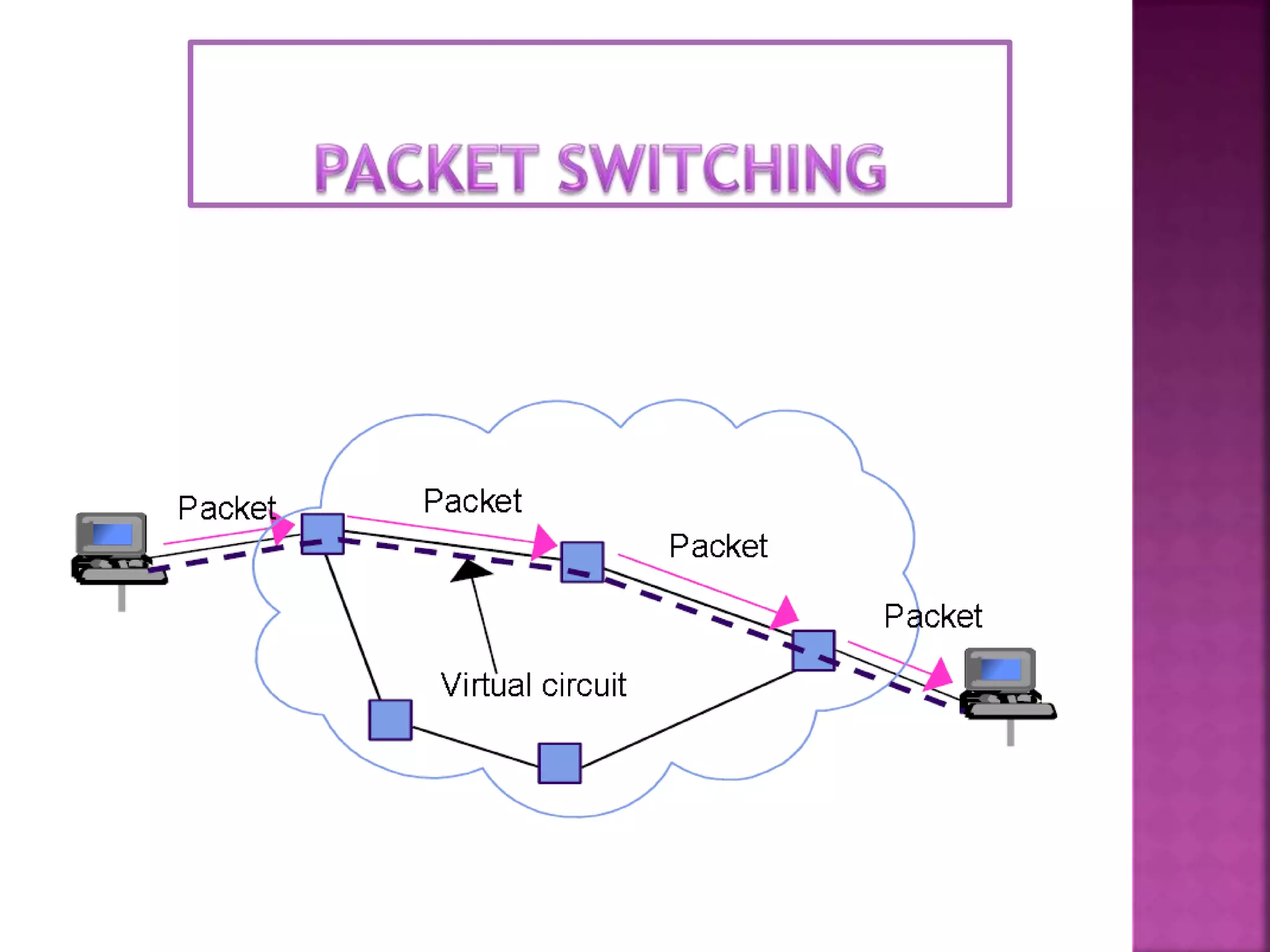
There are three main types of switching used in communication networks: circuit switching, packet switching, and message switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated electrical path between two ports or hosts for the duration of a call. Packet switching breaks communication down into small packets that are routed through a network based on destination addresses. Message switching treats each message as an independent unit that is transmitted from node to node without establishing a direct link between sender and receiver.