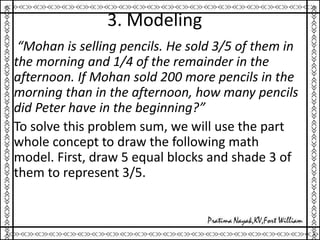
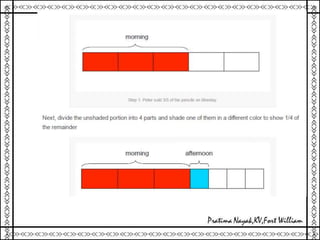
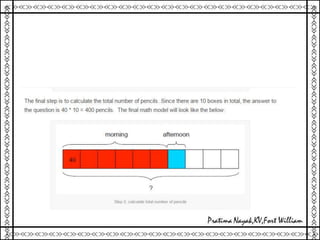
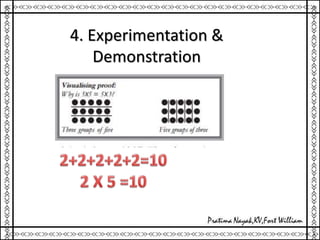
1. The document outlines various methods for engaging students in mathematics education, including hands-on activity-based learning, problem solving, modeling, experimentation and demonstration, self-learning, peer collaboration, and use of online resources.
2. Key aspects of the vision for school mathematics are for children to enjoy rather than fear math, learn important concepts beyond formulas, communicate about math, and see it as meaningful.
3. The teacher's role is to engage every student, help them develop a positive attitude, enjoy math over fearing it, and use more ICT tools for teaching.