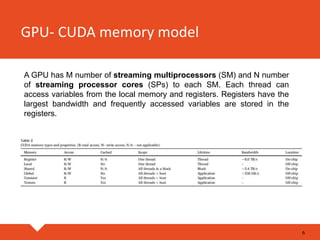
The document discusses the application of GPU CUDA programming in medical image analysis, highlighting its efficiency in processing modalities like CT, MRI, and PET. It covers concepts such as parallel architecture, memory models, and the workflow of CUDA applications, as well as specific tasks like image denoising, registration, segmentation, and visualization. Key algorithms and techniques used in medical image processing, including adaptive filtering and thresholding, are also described.